
Continuous Data Protection: Ensuring Real-Time Information Security
Continuous data protection (CDP) has emerged as a crucial strategy in safeguarding data assets against potential threats and losses. This technology provides real-time, or near-real-time, data backup, minimizing the risk of data loss and enabling quick recovery in the event of an incident. Notably, continuous data protection is widely used by home and small business users, illustrating its versatility and essential role in modern information security practices.
Continuous Data Protection: An Overview
Definition and Key Concepts
Continuous Data Protection (CDP), also referred to as continuous backup or real-time backup, is a method where every change made to data is automatically saved, thus capturing every version of the data that a user saves. This approach allows for restoring data to any point in time, offering a significant advantage over traditional backup methods which only allow data restoration from the last backup point. In an ideal scenario, CDP achieves a Recovery Point Objective (RPO) of zero, meaning no data is lost in the event of an incident, although the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) may not be zero.
CDP operates by continuously recording changes to data as they occur and storing these changes at a secondary location, either on a different system or a specialized appliance. This method does not require backup schedules, which distinguishes it from traditional snapshot-based solutions. Instead, it provides a continuous journal of data changes, enabling precise and granular data recovery capabilities.
Advantages Over Traditional Backup Methods
One of the primary advantages of CDP over traditional backup methods is its ability to provide immediate recovery to any previous state of the data, without the constraints of backup schedules. This capability not only enhances data protection but also significantly reduces the potential for data loss in high-risk scenarios such as malware attacks or system failures.
Traditional backup systems typically operate within a defined backup window, leading to potential data loss for changes that occur between backups. CDP eliminates this risk by continuously capturing data changes, thereby closing the backup window and providing a more robust defense against data loss. This continuous backup process is particularly beneficial in environments where data integrity and availability are critical, such as in financial institutions or healthcare settings where the cost of data loss can be prohibitive.
Furthermore, CDP’s method of only copying changes since the last backup—often referred to as copying the “delta”—uses less storage space and reduces the load on network resources compared to traditional methods that require full periodic backups. This efficiency not only saves on storage costs but also minimizes the impact on system performance, making CDP a cost-effective and less intrusive data protection solution.
In summary, Continuous Data Protection offers a comprehensive security measure by allowing organizations to revert to any previous data state, providing a robust framework against data corruption, and reducing the operational overhead associated with traditional backup methods. This makes CDP an invaluable tool for organizations aiming to maintain high standards of data integrity and availability.
Real-Time Information Security: Why It Matters
Importance of Real-Time Security
Real-time data monitoring transcends routine security measures by enabling the prevention of security threats before they materialize. It is crucial for security professionals to track organizational data access continuously, as this practice provides the capability to manage and oversee data transactions actively. The Ponemon Institute’s 12th annual Cost of Data Breach Study highlights the escalating scale of data breaches, with the average size increasing by 1.8 percent to over 24,000 records, costing approximately $3.62 million on average per breach. These statistics underscore the critical need for robust real-time monitoring systems that offer comprehensive visibility into network systems and a clear understanding of an organization’s security posture.
The Lepide Data Security Platform exemplifies advanced security monitoring by enabling real-time tracking of user activities and system access, which are pivotal for designing effective threat response strategies. This platform facilitates immediate insights into the ‘who, what, where, and when’ of file and folder access, thereby enhancing the ability to address insider threats and meet regulatory compliance requirements.
Impact on Business Operations
Cyber attacks are increasingly sophisticated, making it imperative for organizations to detect and respond to threats as they occur. Real-time threat detection minimizes the damage by reducing the dwell time of threats within networks. By leveraging advanced technologies like AI and machine learning, real-time solutions analyze vast amounts of data across cloud, network, and identity to detect anomalies that traditional methods might miss. This capability not only helps in proactive threat hunting but also in identifying vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
Furthermore, the financial repercussions of cyber incidents are profound. The latest IBM Data Breach Report revealed that 83% of organizations experienced more than one data breach in 2022, highlighting the rampant nature of cyber risks. Public disclosures of cyber incidents have shown that such events can lead to significant economic impacts, including stock price declines and substantial market cap losses. For instance, a ransomware attack on ION Trading Technologies significantly disrupted financial operations, demonstrating how cyber incidents can ripple through the entire supply chain.
Implementing Continuous Data Protection
What Steps Companies need to take to implement Continuous Data Protection?
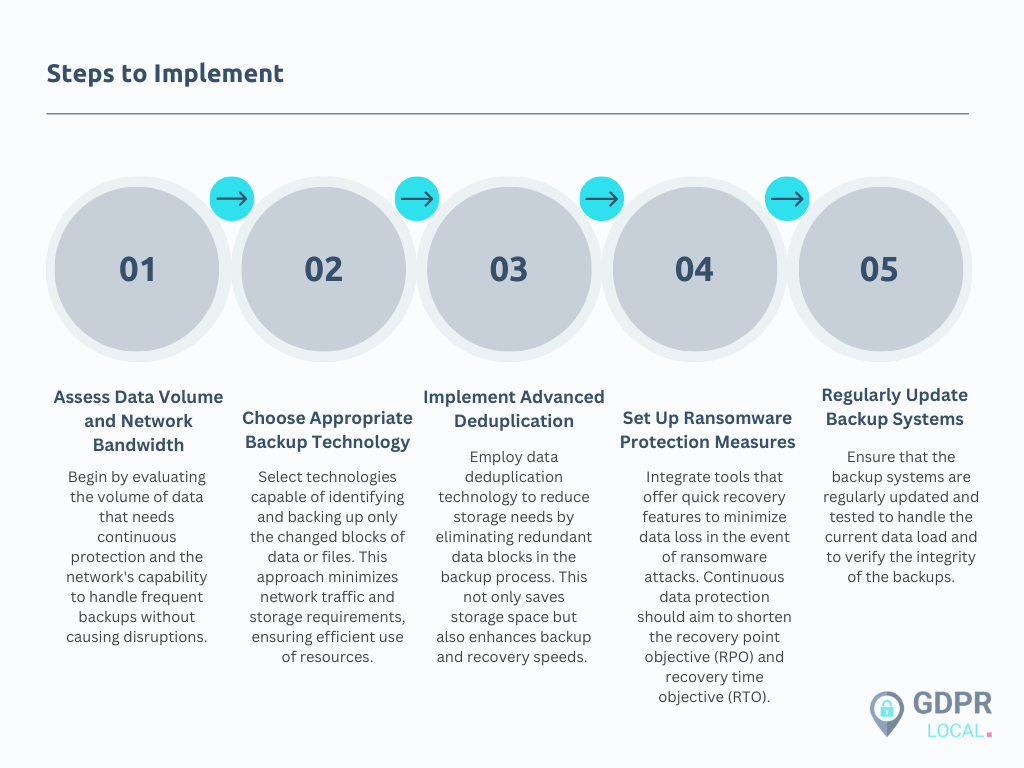
Technology and Tools Required
| Continuous Backup Software | Utilize software that supports continuous data protection by backing up every change as it occurs. This software should provide real-time data replication and allow for instant recovery. |
| High-Performance Storage Solutions | Invest in storage solutions that can handle the high I/O demands of continuous data backups. These should include advanced features like synthetic full backups and should be capable of integrating with existing systems. |
| Network Optimization Tools | Implement tools that can optimize network traffic to prevent saturation during continuous backup processes. These tools help in maintaining network performance while ensuring data is backed up frequently. |
| Immutable Storage Options | Use immutable storage solutions like Ootbi for critical backups. These solutions prevent data alteration, providing a secure environment for backup data and enabling effective recovery from ransomware attacks. |
| Monitoring and Reporting Tools | Deploy monitoring solutions that provide real-time insights into backup status and alert administrators about potential issues in the data protection process. These tools are vital for maintaining operational continuity and ensuring data integrity. |
Implementing continuous data protection involves careful planning and the integration of advanced technologies designed to minimize data loss and ensure quick recovery in the event of data corruption or loss.
Challenges and Solutions in Continuous Data Protection
Common Challenges
Continuous data protection (CDP) faces several challenges that can impede its effectiveness and scalability within an organization. One significant challenge is the ability of CDP systems to scale with organizational growth. Some CDP solutions are designed for smaller data sets and may experience a degradation in processing speed as data volume increases or as more applications are integrated. This can necessitate the integration of supplemental or redundant storage and processing solutions, which not only requires additional time but also potentially delays opportunities for data analysis and utilization.
Additionally, the corporate culture of an organization can significantly impact the success of CDP implementation. A culture that does not prioritize cybersecurity can undermine data protection efforts. Moreover, the complexity of modern IT environments, such as large-scale cloud infrastructures and containerized applications, adds another layer of challenge, demanding a more robust approach to data protection.
Security threats, including social engineering attacks like phishing, pose unique challenges to data protection strategies. The physical security of data is also a concern, especially in scenarios where physical workspaces are left unoccupied, as seen during the COVID-19 pandemic, making organizational assets more vulnerable to theft or damage.
Effective Solutions
To overcome these challenges, organizations need to adopt a strategic approach to implementing CDP. Initially, it is crucial to ensure the chosen CDP can scale effectively. Organizations should opt for CDP solutions that are capable of scaling up or down as requirements change, without significant alterations to the data architecture. These solutions should ideally support larger datasets and include robust security and governance frameworks to enhance compliance and data privacy.
Involving all stakeholders from the outset is vital for successful CDP implementation. Documenting all use cases and ensuring that non-technical staff understand and are trained in the use of CDP is crucial for broad adoption and effective use. This includes showing non-technical teams, like marketing, features they can utilize early on, such as data insights for strategic decision-making.
Adopting low code/no-code tools can also facilitate wider adoption by enabling non-technical users to create applications and access customer data securely, thus enhancing operational flexibility. Additionally, choosing CDP solutions with out-of-the-box connectors for preferred source systems can minimize the need for manual customization and accelerate the integration process.
Addressing the broader challenges involves changing the corporate culture to take cybersecurity seriously. This might include educating senior executives and board members about the risks and financial implications of inadequate data protection. Implementing basic security measures and advancing to more complex solutions progressively can help in building a robust defense against both physical and cybersecurity threats.
Conclusion
This technology, highlighted for its real-time backup capabilities, emerges as an essential strategy for ensuring that organizations can quickly recover in the wake of cybersecurity incidents. By reflecting on the advantages of CDP over traditional backup methods, including its ability to offer immediate recovery and minimize data loss risks, it’s evident that CDP stands out as an invaluable tool for maintaining data integrity and availability in our increasingly digital world.
In adopting CDP, organizations face challenges, yet the detailed solutions outlined demonstrate practical ways to surmount these obstacles, ensuring effective implementation. The significance of embracing a continuous data protection strategy cannot be overstated, especially in an era where data is both a vital asset and a target for sophisticated cyber threats. As we conclude, let us recognize the imperative of continuous data protection in safeguarding the lifeline of modern businesses. Emphasizing the broader implications, the journey towards robust real-time information security is both a strategic necessity and a pathway to sustaining business resilience in the digital age.
FAQs
Can you provide an example of how continuous data protection operates?
Continuous data protection (CDP) involves replicating the backup store to a remote data center at frequent intervals. Additionally, CDP maintains multiple versions of each file, enabling users to revert to earlier versions if necessary.
What does continuous data protection entail?
Continuous data protection is a strategy for real-time data backup that records every change made to the data. This allows files to be restored to any previous state, providing a robust solution for data recovery.
How does continuous data protection differ from traditional backup methods?
Unlike traditional backup methods that usually save data at the file level during scheduled times, continuous data protection (CDP) operates at the block level and backs up data immediately as any changes occur. This method eliminates the need for scheduled nightly backups and provides more immediate data recovery options.
What platforms are supported by continuous data protection for achieving near-zero Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs)?
Trilio’s continuous data protection software supports platforms that allow for near-zero RPOs and Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs), significantly reducing downtime and preventing data loss during outages or disasters.