
Data Protection Handbook: Protecting Your Digital Assets in 2024
As the digital landscape continues to grow rapidly, safeguarding digital assets has evolved from a precautionary measure to an absolute necessity. Understanding data protection and implementing strong principles and policies is essential for both individuals and businesses to protect themselves from cybersecurity threats, data breaches, and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
The essentials of data protection are crucial for anyone looking to evaluate their current data security measures, understand key protection principles, and develop an effective policy. By focusing on the critical steps needed to build a strong data protection strategy, individuals and organizations can gain the knowledge and tools necessary to secure their digital assets in the years to come.
Data Protection: An Overview
Definition and Importance
Data protection is the process of protecting important and valuable information from corruption, compromise, or loss. It involves the capacity to restore data if it is made unavailable or corrupted by a security breach or operational incident. This is crucial not only for individuals but also for organizations that collect, store, process, or share personal data, as it enhances their cybersecurity, preserves reputation, saves time and money, and enhances customer trust.
Types of Data Protection
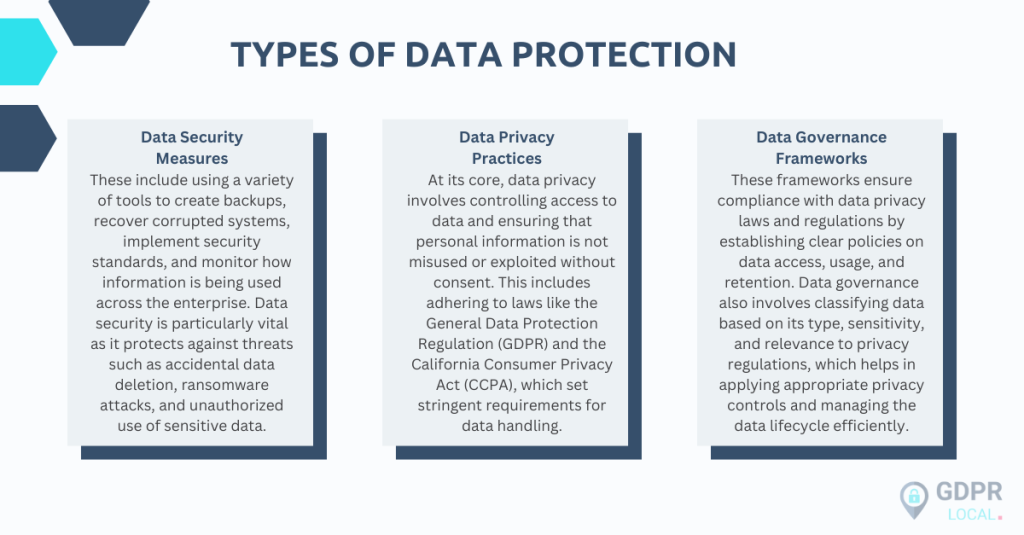
Assessing Your Current Data Security
Identifying Vulnerabilities
When assessing current data security, identifying vulnerabilities is a crucial first step. Organizations should start by evaluating their IT systems, underlying infrastructure, support systems, and major applications for weaknesses. This includes analyzing potential exposures generated by the supply chain and business partners. Vulnerability identification allows organizations to understand the weaknesses in their system from the perspective of a potential attacker, which is vital to proactively protect the system rather than reactively addressing issues post-attack.
Public-facing web applications, often primary threat vectors, should be rigorously assessed to determine how attackers could infiltrate the organization’s IT systems. It’s essential to evaluate and provide remediation recommendations for the spectrum of web applications, considering the inherent weaknesses built into many deployed applications due to the development process and tools used.
Evaluating Current Measures
After identifying vulnerabilities, evaluate the current cybersecurity measures in place. This involves reviewing the organization’s adherence to comprehensive cybersecurity frameworks like GDPR, ISO/IEC 27001, and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. These standards and frameworks provide a structured approach to managing information security and include requirements for the assessment and treatment of information security risks tailored to the needs of the organization.
Regular security audits are a must to ensure that security measures are up-to-date and effective against evolving threats. These audits help identify and address vulnerabilities, ensuring the security infrastructure can withstand current and future challenges. Additionally, training employees on cybersecurity best practices is fundamental. This not only helps in recognizing phishing attempts and using strong passwords but also in securely handling sensitive data, significantly reducing the risks posed by human errors.
Organizations should also implement effective data protection strategies that involve multi-step processes to minimize the footprint of sensitive data and secure business-critical and regulated data. This includes using data encryption, implementing antivirus software, and establishing perimeter security hardware and software. Continuous monitoring and reviewing processes are necessary to gain visibility into data activities, risks, and controls, which aids in improving protection and responding to threats and anomalies.
By combining these measures with proactive vulnerability identification and regular evaluations of current security measures, organizations can enhance their data protection and significantly mitigate the risks associated with data breaches and other cybersecurity threats.
Essential Data Protection Measures
Encryption Techniques
Encryption serves as a fundamental component in safeguarding data, ensuring that sensitive information remains inaccessible to unauthorized parties. By utilizing complex algorithms, encryption transforms readable data into a secure format that can only be deciphered with a specific key. Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a widely trusted method, providing robust protection with key sizes of 128, 192, and 256 bits. For organizations managing highly sensitive data, employing strong encryption methods like AES-256 or RSA ensures that data remains secure, whether in transit or at rest.
Utilizing Firewalls and Antivirus Software
Firewalls are critical in defending against unauthorized access and cyber threats, acting as a barrier that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules. They range from basic packet filtering firewalls, suitable for small networks, to more sophisticated Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs) that integrate additional features such as intrusion prevention and deep packet inspection for enterprise environments. Similarly, antivirus software plays an essential role in protecting digital assets by detecting, quarantining, and removing malicious software. Modern antivirus solutions employ a combination of signature-based and behavior-based detection techniques to effectively identify and block potential threats.
Regular Backups
Regular data backups are a critical strategy for ensuring data integrity and availability in the face of data loss incidents. By maintaining frequent backups, organizations can quickly restore lost or corrupted data, minimizing downtime and operational disruptions. Implementing a robust backup strategy involves using reliable backup software that supports features like incremental backups and encryption, ensuring backups are up-to-date and secure. Additionally, following the 3-2-1 backup rule-keeping at least three copies of data on two different media, with one stored offsite-provides a comprehensive approach to safeguarding valuable digital assets against various types of data loss.
Developing a Data Protection Strategy
Creating a Data Protection Plan
A Data Protection Policy (DPP) is essential for any organization aiming to systematize the utilization, oversight, and governance of data. It serves not only to safeguard and secure all data handled, stored, or processed by the organization but also ensures compliance with data protection standards and regulations. The scope of a DPP should be comprehensive, covering data in on-site storage, remote locations, and cloud-based services, thus fortifying the security and integrity of data both at rest and in transit.
The initial section of a DPP should clearly define its scope, including the types of personal data collected, processed, and stored, and the purposes for which this data is used. This ensures the organization addresses data protection issues and complies with regulations. Furthermore, the policy should encompass any third-party service providers, ensuring they adhere to the same data protection standards, especially critical if personal data is transferred across borders.
Implementing Policies and Procedures
The development of a data protection policy involves establishing clear definitions for key terms such as personal data, processing, data controller, and data processor, which aids in mutual understanding among all stakeholders. This policy should reflect core principles of data protection such as lawfulness, fairness, transparency, and accountability as outlined by regulations like the GDPR.
Organizations must outline lawful bases for processing personal data and provide guidelines on obtaining consent. It is also crucial to assign clear roles and responsibilities for data protection, defining the roles of data controllers, processors, and protection officers, and outlining their specific duties. In case of a data breach, the policy should include procedures for breach notification and measures to prevent future incidents.
Employee Training and Awareness
Data privacy training is vital in fostering a culture of data protection within an organization. Training programs should educate employees about data privacy regulations, company policies, and the importance of protecting sensitive information. These programs should cover compliance training, security best practices, and the significance of recognizing social engineering attempts and unauthorized access.
Regular training updates are necessary to equip employees with the skills to handle data securely and make informed decisions concerning data privacy. This not only helps in preventing data breaches but also prepares employees to act swiftly and effectively in case of data privacy incidents.
Conclusion
Reflecting on the significance of developing an effective data protection policy, the discussions underscored the indispensability of continuous monitoring, vulnerability assessment, and employee training in ensuring data integrity and compliance with global standards.
Let this article serve as a catalyzer for further research and action towards fortifying your digital assets against the evolving landscape of cyber threats, ensuring a secure digital future for all.