
Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIA): A Practical Guide (Updated 2025)
If you’ve ever delved into data protection, you’ve likely come across the term Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA). But what exactly does it mean, and what does it involve? In this guide, we’ll explore what DPIAs are and why they matter. We’ll walk you through the steps to conduct a DPIA, from identifying the need for one to implementing safeguards. We’ll also discuss common challenges you might face when doing a DPIA and share best practices to overcome them. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to use DPIAs to enhance your data protection efforts and minimize risks to personal information.
What is a DPIA?
A Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) is a process we use to identify and minimize data protection risks. It’s a key part of our accountability under the GDPR and helps us comply with our data protection obligations. We use DPIAs to systematically analyze, identify, and reduce the data protection risks of a project or plan.
What are the benefits of conducting a DPIA?
DPIAs are more than just a box-ticking exercise. They’re a living process that helps us manage and review the risks of data processing on an ongoing basis. By doing a DPIA, we improve our awareness of the data protection risks associated with a project, which in turn helps us improve its design and enhance our communication about privacy risks with stakeholders.
How do I know if I should conduct a DPIA?
We’re required to conduct a DPIA when our processing is likely to result in a high risk to individuals’ rights and freedoms. This is particularly relevant when we introduce new data processing technology.
Here are some specific situations where a DPIA is mandatory:
1. Systematic and extensive profiling with significant effects
2. Large-scale use of sensitive data
3. Public monitoring
It’s also good practice to do a DPIA for any major project involving personal data use. If we fail to carry out a DPIA when required, we could face enforcement action, including a fine of up to £8.7 million or 2% of our global annual turnover if higher.
Key Components of a DPIA
A DPIA should include several key elements:
1. A description of the processing operations and purposes
2. An assessment of the necessity and proportionality of the processing
3. An assessment of the risks to individuals’ rights and freedoms
4. The measures we plan to take to address these risks
Let’s break these down further:
Description of Processing
This includes the nature, scope, context, and purposes of the processing. We need to consider how we collect, store, use, and share the data, who has access to it, and whether we’re using any new technologies or novel types of processing.
Necessity and proportionality
We need to consider whether our plans help achieve our purpose and if there’s any other reasonable way to achieve the same result.
Risk assessment
We need to assess both the likelihood and severity of potential harm to individuals. This could include illegitimate access to data, unwanted modification, or data loss.
Risk mitigation
For each identified risk, we need to consider options for reducing it. This could include staff training, data anonymization, or implementing new systems to help individuals exercise their rights.
It’s important to note that we don’t always have to eliminate every risk. Sometimes, we may decide that some risks are acceptable given the processing’s benefits and the mitigation’s difficulties. However, if there’s still a high risk after taking additional measures, we need to consult the ICO before proceeding with the processing.
By conducting a DPIA, we’re not just complying with legal requirements. We’re also supporting the principle of data protection by design and default, as required by Article 25 of the UK GDPR. This approach helps us build in data protection compliance at an early stage when there’s the most scope for influencing how the proposal is developed and implemented.
Remember, a DPIA is a flexible tool. We can design a process that fits with our existing approach to managing risks and projects, as long as it contains these key elements. The goal is to create a process that works for us while ensuring we’re thoroughly assessing and addressing data protection risks.
Conducting a DPIA: Step-by-Step Guide
We’ll now walk through the key steps of conducting a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA). This process is crucial for identifying and minimizing data protection risks associated with our projects or plans.
Description of the Processing
The first step is to provide a detailed description of how we plan to use personal data. We need to cover the nature, scope, context, and purposes of the processing. Here’s what we should include:
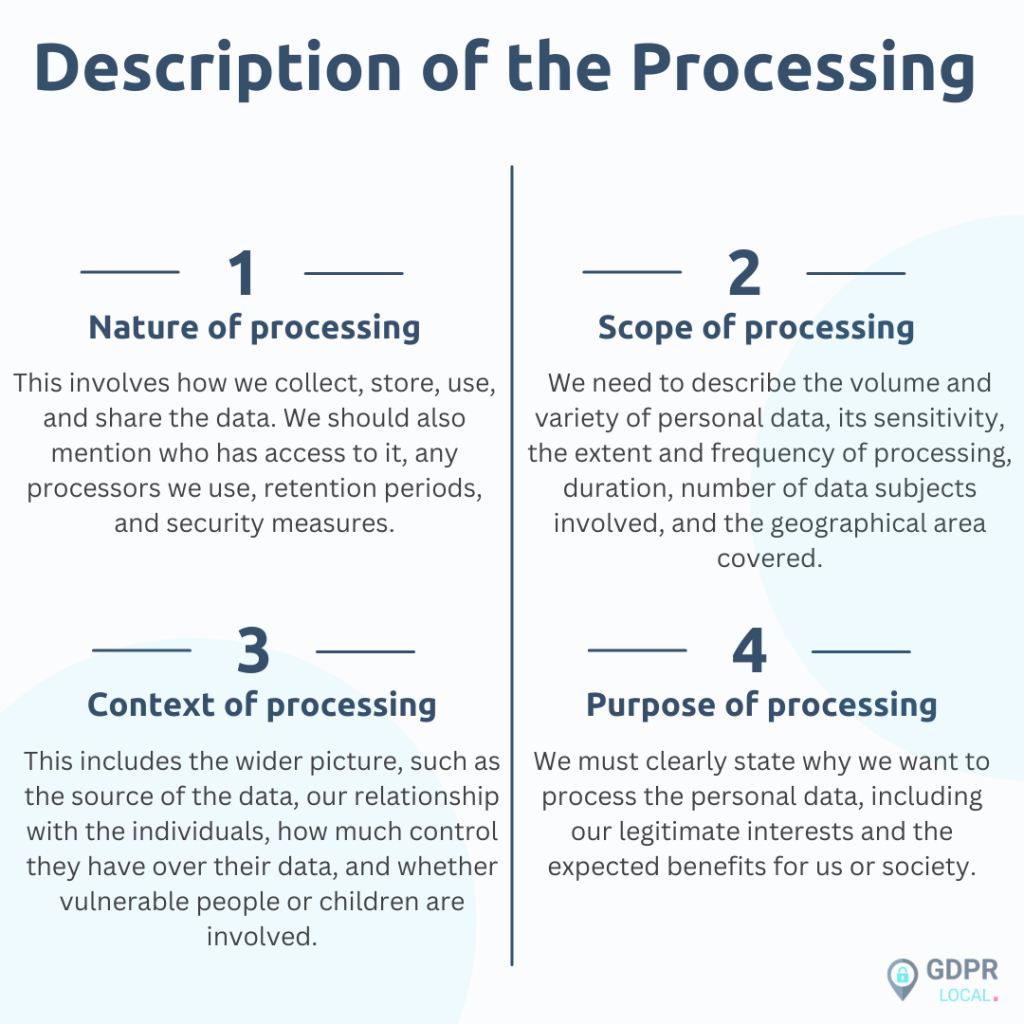
Assessing Necessity and Proportionality
Next, we need to evaluate whether our plans are necessary and proportionate to achieve our purpose. We should consider:
1. If our plans help achieve our purpose
2. If there’s any other reasonable way to achieve the same result
We also need to demonstrate how we ensure data protection compliance. This includes:
– Our lawful basis for processing
– How we’ll prevent function creep
– Measures to ensure data quality and minimization
– How we’ll provide privacy information to individuals
– How we’ll implement and support individuals’ rights
Identifying and Evaluating Risks
In this step, we assess the potential impact on individuals and any harm our processing may cause . We should look at risks such as:
| Inability to exercise rights | Financial loss |
| Loss of control over personal data | Reputational damage |
| Discrimination | Physical harm |
| Identity theft or fraud | Loss of confidentiality |
It’s important to note the magnitude of these risks, considering both the likelihood of a risk occurring and its impact. We should keep a record of all identified risks, which will help us create solutions later in the DPIA process.
Implementing Safeguards
Finally, we need to identify measures to mitigate the risks we’ve identified. For each risk, we should:
1. Record its source
2. Consider options for reducing the risk
Some examples of safeguards include:
– Training staff to anticipate and manage risks
– Anonymizing or pseudonymizing data where possible
– Writing internal guidance or processes
– Using different technologies
– Implementing clear data-sharing agreements
– Making changes to privacy notices
– Offering individuals the chance to opt out where appropriate
We should record whether each measure would reduce or eliminate the risk, taking into account the costs and benefits of each option.
By following these steps, we can conduct a thorough DPIA that helps us identify and address data protection risks effectively. This process not only ensures compliance with GDPR but also builds trust with our users by demonstrating our commitment to protecting their personal data.
Challenges and Best Practices in DPIA Implementation
Implementing a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) comes with its own set of challenges. However, by following best practices, we can overcome these hurdles and ensure a smooth DPIA process. Let’s explore some key areas we need to focus on.
Stakeholder Engagement
One of the biggest challenges in conducting a DPIA is getting accurate and timely information from all relevant stakeholders. To address this, we need to involve a wide range of people in the process.
We should start by engaging our data protection officer (DPO) if we have one. Their advice is crucial in determining whether we need a DPIA, how to conduct it, and what measures we can take to mitigate risks. It’s important to record our DPO’s advice and justify any decisions that don’t align with their recommendations.
We also need to involve the project team and other relevant departments. A wide internal consultation can uncover data protection risks that might only be apparent to individuals working on specific aspects of the project. This includes engineers, designers, and developers who have practical knowledge of the operations.
To get a complete picture, we should consider consulting with external stakeholders as well. This might include bringing in external specialists if our organization lacks sufficient expertise or if a project holds a very high level of risk. We should also think about how to consult individuals or their representatives, perhaps through focus groups or surveys.
Documentation
Good documentation is crucial for demonstrating compliance with GDPR and minimizing legal risks. We need to keep detailed records of our DPIA process, including:
1. The scope of the assessment
2. Our data mapping exercise
3. Risk assessment and management strategies
4. Any other relevant information
It’s important to keep this documentation up to date and make it available to relevant stakeholders if requested. Some organizations find it challenging to document past actions and assessments, especially when using spreadsheets. We might want to consider using specialized tools to make this process more manageable.
Continuous Review
A DPIA isn’t a one-time exercise. It’s an ongoing process that needs to be integrated into our organizational processes. This continuous approach helps us stay on top of changing risks and ensures our data protection measures remain effective.
We need to monitor the ongoing performance of our DPIA and be prepared to cycle through the process again before our plans are finalized. It’s a good idea to set up a review schedule and keep track of any actions that result from these reviews.
We should be ready to repeat the DPIA if there’s a substantial change to the nature, scope, context, or purposes of our processing. This might happen as our organization and processes evolve over time.
By treating the DPIA as an ongoing process, we can improve awareness of data protection risks within our organization. This approach helps us enhance the design of our projects and improve how we communicate about data privacy risks with relevant stakeholders.
Implementing these best practices can be challenging, but the benefits are significant. A well-executed DPIA not only ensures compliance but can also yield efficiency benefits by helping us streamline our information-handling processes. It improves our project designs and enhances our communication about data privacy risks.
Remember, transparency is key throughout the DPIA process. Consider publishing your DPIA to foster trust in your processing activities and improve individuals’ ability to exercise their rights. By being open about our data protection efforts, we can build stronger relationships with our stakeholders and demonstrate our commitment to privacy.
When don’t I need to conduct a DPIA?
You don’t need to conduct a DPIA if the data processing is unlikely to result in a high risk to the rights of individuals. For example, if your project involves standard, low-risk processing that doesn’t include sensitive data, large-scale monitoring, or profiling, a DPIA probably isn’t necessary. Routine activities such as processing employee contact details for payroll or collecting email addresses for a company newsletter (with proper consent) typically don’t trigger the DPIA requirement. However, you should still document your decision and be prepared to explain your reasoning. If you’re unsure, it’s best to consult your DPO or conduct a DPIA screening assessment to determine whether a full DPIA is required. Taking this step shows accountability and reinforces your commitment to protecting personal data.
What should I do after conducting a DPIA?
After completing a DPIA, you should review and approve the assessment outcomes internally. Make sure all identified risks have appropriate safeguards in place and document the decisions made during the process. If any high risks remain that you cannot mitigate, you must consult with the relevant supervisory authority, such as the ICO, before starting the processing. Share the results with key stakeholders and integrate the risk mitigation actions into your project plan. Update your privacy documentation, including policies and notices, to reflect changes. Most importantly, the DPIA should be treated as a living document. Monitor your project regularly and revisit the DPIA if there are any significant changes to how you process personal data. This ongoing approach ensures your processing stays compliant and your data protection measures remain effective.
Conclusion
The implementation of DPIAs comes with challenges, but these can be overcome through best practices such as engaging stakeholders, maintaining thorough documentation, and conducting ongoing reviews. By treating DPIAs as a continuous process rather than a one-time exercise, organizations can stay ahead of evolving risks and demonstrate their commitment to data protection. This approach not only ensures compliance but also yields benefits in terms of improved project design and communication about privacy risks.
FAQs
What are the key phases involved in conducting a DPIA?
A DPIA should include the following stages: outlining the nature, scope, context, and purposes of the data processing; evaluating the necessity, proportionality, and compliance of the processing measures; identifying and assessing the risks posed to individuals by the processing; and determining any additional measures to mitigate those risks.
What is a DPIA, and under what circumstances is it mandatory?
A Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) is mandatory in several scenarios, such as when there is a systematic and extensive evaluation of personal aspects relating to individuals, which includes profiling, or when there is large-scale processing of sensitive data or systematic monitoring of publicly accessible areas.
Who is responsible for completing a DPIA?
The responsibility for conducting DPIAs can be assigned within your organization or outsourced. However, the ultimate responsibility for the DPIA rests with your organization. If your organization has a Data Protection Officer (DPO), their advice must be sought and documented as part of the DPIA process.
What does the DPIA process entail?
The DPIA process involves describing the personal data that will be processed, the purposes and justifications for using this data, and assessing the necessity and proportionality of processing this data relative to your goals. It also includes evaluating the privacy risks associated with the data processing.