DPIA vs PIA: What’s the Difference and Why It Matters
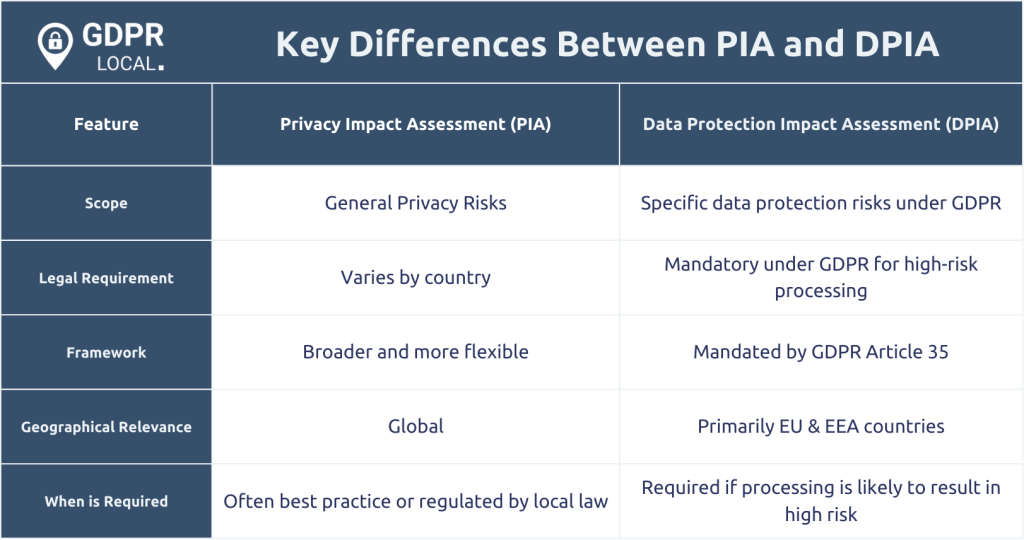
Privacy risk assessments are crucial for ensuring compliance with privacy laws and building trust with users. Two commonly referenced types of privacy assessments are the Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) and the Privacy Impact Assessment (PIA). While they share similarities, they serve slightly different purposes and are rooted in different legal and regulatory frameworks. Understanding the distinction between DPIA and PIA can help organisations make informed decisions about data protection and compliance.
Key Takeaways
• DPIA is GDPR-mandated for high-risk processing activities – Under Article 35 of the GDPR, a DPIA is legally required when processing operations are likely to result in a high risk to the rights and freedoms of data subjects, particularly in cases involving profiling, large-scale sensitive data, or systematic monitoring.
• PIAs offer broader risk-scoping across jurisdictions – PIAs are adaptable frameworks for assessing privacy risks, often aligning with non-EU legal systems or organisational privacy programs. They support risk identification across various data types and use cases, without being tied to a single regulatory standard.
• Assessment scope and triggers vary by legal framework – While DPIAs have defined triggers and content requirements (e.g., risk assessments, mitigation plans, DPO consultation), PIAs are more flexible in scope and methodology, allowing organisations to tailor assessments based on local legal obligations and internal policies.
What is a PIA?
Privacy Impact Assessment (PIA) is a comprehensive tool used to evaluate the impact of a project, system, or process on the privacy of individuals. It helps identify potential privacy risks and propose mitigation strategies to minimise those risks.
Originally developed as a best practice, PIAs are now a requirement in many jurisdictions. They are typically conducted in the early stages of a project to ensure privacy risks are considered before implementation.
Key Features of a PIA:
• Identifies how personal data is collected, used, stored, and shared;
• Assesses risks to individual privacy;
• Recommends strategies for minimising those risks;
• Often used in both the public and private sectors;
• Can be required under various national laws (e.g., Canada, Australia, U.S. federal guidelines).
What is a DPIA?
Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) is a specific type of privacy impact assessment required under the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). It is mandatory when data processing is likely to result in a high risk to the rights and freedoms of individuals.
DPIAs are more prescriptive than general PIAs and have specific criteria under the GDPR that trigger their necessity. They’re particularly relevant for activities such as large-scale processing of sensitive data, profiling, surveillance, or the implementation of new technologies.
How to Prepare for a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA)
Preparing for a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) involves a structured approach to identify, assess, and mitigate risks associated with data processing activities. Start by mapping out the data flows: what data is collected, how it’s processed, stored, shared, and eventually deleted. Engage key stakeholders early, including legal, compliance, IT, and your Data Protection Officer (DPO), to ensure a comprehensive view. It’s essential to understand the purpose and legal basis for processing, especially when sensitive or high-risk data is involved.
Documenting each step, assessing potential impacts on individuals’ rights, and defining mitigation measures will not only streamline the DPIA process but also demonstrate accountability and compliance with data protection regulations.
Key Features of a DPIA:
• Mandatory under GDPR for high-risk data processing;
• Must include a systematic description of the processing;
• Requires assessment of necessity, proportionality, and risks;
• Involves consulting with the Data Protection Officer (DPO);
• May require consultation with supervisory authorities if risks can’t be mitigated.
Which One Do You Need?
The type of assessment you need depends on your location, the nature of your project, and the legal frameworks you must comply with. If you’re operating within the European Economic Area (EEA) or processing EU citizens’ data, a DPIA may be legally required. For organisations outside of the EU, a PIA might be the standard approach, especially if guided by national regulations or industry best practices.
In some cases, organisations may choose to conduct both, using a PIA as a broader framework and embedding DPIA requirements where applicable.