
Top Techniques for Data Classification and GDPR Compliance
Data classification is important for GDPR compliance. By properly categorising personal data, organisations can protect their data and comply with the GDPR. This article outlines the top techniques for data classification, enabling you to understand how to protect personal data and comply with the GDPR.
Key Takeaways
• Data classification is essential for GDPR compliance, enabling organisations to safeguard personal data and implement appropriate security measures based on sensitivity levels.
• A comprehensive data classification policy should outline goals, procedures, and roles while utilising automated tools for efficiency and accuracy in handling large volumes of data.
• Integrating data classification with security measures, such as encryption and access controls, enhances data protection and minimises the risks of unauthorised access and breaches.
Understanding Data Classification
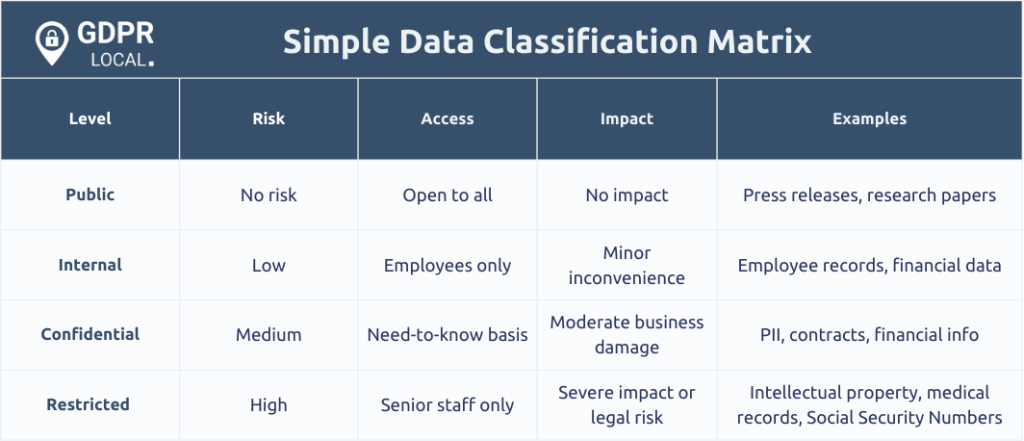
Data classification refers to the process of organising and categorising data based on its sensitivity and importance. This fundamental practice is crucial for managing personal and sensitive data effectively, ensuring that appropriate security measures are in place to protect it from unauthorised access and breaches. Classifying data enables organisations to prioritise resources, enhance data security, and comply with regulatory requirements, such as the GDPR.
The importance of data classification in the context of GDPR cannot be overstated. It enables organisations to enforce strict data handling requirements, protect personal data, and maintain compliance with data protection regulations. Personal data, such as names, addresses, and email addresses, must be classified to ensure they are handled with the necessary care and security.
Implementing a comprehensive data classification policy lays the foundation for an effective data privacy compliance program, enhancing overall data security by segregating data based on its sensitivity.
How Data Classification Works
Data classification involves several key steps, starting with defining a classification schema that categorises data based on its sensitivity levels. This schema helps determine if sensitivity-based protections are present and enforced, ensuring that confidential data is kept within the organisation and accessed only by authorised personnel. The process can be executed manually, using human judgment, or automatically, leveraging algorithms and machine learning techniques.
A crucial aspect of data classification is data mapping, which involves identifying where customer data resides, who has access to it, and how it is processed. Once data is classified, organisations can implement appropriate security controls and policies, such as encryption and access controls, tailored to the sensitivity of the data. Automated data classification systems offer improved accuracy and significantly reduce the time required for classification, making them an attractive option for organisations dealing with large volumes of data.
Effective data classification requires considering the types of data handled, their sensitivity levels, and relevant regulatory requirements, including data classification standards. Types of data typically included in classification efforts are personally identifiable information (PII), protected health information (PHI), financial data, and classified personal data.
Prioritising resources based on data sensitivity enables organisations to manage, protect, and handle their data assets efficiently.
Why Data Classification Matters for GDPR
Data classification is a cornerstone of GDPR compliance, as it protects sensitive information, identifies critical assets, and allocates appropriate security measures. By classifying data, organisations can achieve, maintain, and prove compliance with GDPR, mitigating the risks associated with unorganised data. Non-compliance with GDPR can result in hefty fines, penalties, and damage to an organisation’s reputation, making proper data classification essential.
Effective data classification increases data visibility, reallocates resources, minimises operational risks, and ensures compliance with regulations. It allows organisations to tailor their security measures and governance controls, enhancing overall data protection. Proper data categorisation also strengthens security protocols against unauthorised access and breaches, providing substantial benefits beyond regulatory compliance.
Adopting effective data classification practices helps organisations build trust with partners and customers, showcasing their commitment to data protection. Timely and accurate data classification supports organisations in respecting individual privacy rights, fostering a robust culture of data protection and increasing overall trust.
Key Elements of GDPR Compliance
Achieving GDPR compliance requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses various elements, including understanding the definitions of personal and sensitive data, as well as adhering to data protection principles. Employing data classification techniques helps organisations identify and protect individual and sensitive data, ensuring they meet regulatory requirements and enhance their compliance efforts.
Real-world implementations of data classification demonstrate its practical impact on organisations’ abilities to meet GDPR obligations.
Personal Data and Sensitive Data
Under GDPR, personal data refers to any information related to a natural person or data subject. This can include details that identify or could potentially identify someone, protecting personal data. This includes standard identifiers, such as home addresses and contact information, as well as more specific categories, including genetic data and health information.
Sensitive personal data encompasses categories such as racial or ethnic origin, genetic information, and health information, which are subject to stricter rules governing the processing of personal data. With the rise of global privacy laws, adaptive data classification strategies are crucial for ensuring compliance.
Data Protection Principles
The GDPR outlines several key principles of general data protection regulation that organisations must adhere to, including accountability, data minimisation, and accuracy. Data classification plays a vital role in complying with these principles by ensuring organisations maintain accurate records of personal data handling and collect only the data necessary for legitimate purposes, in accordance with data protection laws.
Classifying health data, for example, helps healthcare organisations minimise risks associated with unauthorised access and data breaches. Effective data classification practices are crucial for managing rights, including data access and the right to be forgotten, under new regulations.
Implementing a Data Classification Policy
Creating and implementing a data classification policy is crucial for organisations that aim to protect personal data and comply with the GDPR. A well-defined policy should outline goals, procedures, roles, responsibilities, and compliance mandates, including those of a data protection officer. It promotes a culture of compliance and ensures the security of confidential information.
Organisations should consider industry-specific requirements and the types of data that regulators scrutinise when implementing data classification. Building relationships with team members who are most involved in the data is also crucial for effectively applying a data classification framework.
Training and clear communication are crucial for the successful implementation of policies.
Setting Up Data Categories
Defining clear data categories is the first step in setting up a data classification policy. These categories should reflect the significance and sensitivity of the data, ensuring uniformity in classification across the organisation.
Involving key stakeholders in the classification processes ensures comprehensive coverage of organisational needs and enhances the effectiveness of the classification policy.
Assigning Data Owners
Data owners play a critical role in managing and protecting specific data categories, ensuring appropriate security measures are in place. Regular reviews of data classification practices help organisations adapt to changing compliance needs, ensuring that the data classification scheme remains practical and up-to-date.
Documenting and Communicating Policies
Thorough documentation of data classification policies is essential for ensuring consistency in enforcement across the organisation. The process should involve various stakeholders, including IT, legal, compliance, and communications teams, to provide comprehensive policy development.
Training and involving stakeholders in policy implementation help address resistance to change and ensure that new hires understand the classification policies.
Practical Steps for Effective Data Classification
Effective data classification starts with understanding the data landscape and setting clear objectives and scope. Emerging trends, such as data discovery and the integration of AI and machine learning, are simplifying the modelling process and enhancing transparency in decision-making.
Regular audits and reviews are essential to adjust data classification practices in response to evolving business objectives and changing legal requirements.
Utilising Automated Tools
Automated data classification tools can significantly enhance accuracy and efficiency in identifying sensitive data. These tools utilise machine learning algorithms to analyse large datasets quickly, streamlining the data classification process and ensuring better compliance with GDPR.
Regular Audits and Updates
Regular audits are crucial for ensuring that data classification remains effective and compliant with the GDPR. Organisations should regularly assess and update their data classification schemes to adapt to evolving data and regulatory environments.
This ensures scalability and ongoing compliance.
Integrating Data Classification with Security Measures
Integrating data classification with security measures allows organisations to prioritise security controls based on data sensitivity. Classifying data enables organisations to implement targeted security controls, ensuring that sensitive data is effectively protected. Specific security measures, such as encryption and access controls, can be tailored to the sensitivity of the data.
Automated scanning tools further enhance the accuracy of data classification, leading to better security outcomes by minimising human error.
Access Controls
Access controls should be aligned with the sensitivity classification of data to effectively mitigate unauthorised access. In the healthcare sector, for example, implementing access controls and data classification helps manage protected health information (PHI) in compliance with GDPR, ensuring sensitive data is handled securely and access is controlled.
Data Encryption
Sensitive data typically requires encryption both during storage and transmission to protect it against a data breach and to implement effective data protection measures.
Healthcare providers, for example, utilise effective data classification systems to manage PHI and safeguard patient data in accordance with GDPR.
Data Backup and Recovery
A robust data backup strategy is essential for minimising data loss and ensuring business continuity in the face of unforeseen events. The backup strategy should reflect the classification level of the data, with higher-sensitivity data requiring more frequent backups.
Case Studies: Data Classification in Action
Real-world examples illustrate the benefits of data classification in achieving GDPR compliance. For instance, a financial institution implemented a robust data classification framework to identify and protect sensitive customer data, ensuring compliance with GDPR. Data classification examples can further demonstrate these benefits in various sectors.
Similarly, a healthcare provider successfully managed protected health information (PHI) by implementing data classification strategies that ensured patient data was handled in accordance with GDPR requirements. These case studies demonstrate how effective data classification enhances compliance, protects sensitive information, and fosters trust and transparency.
Financial Services
The financial services sector often handles vast amounts of sensitive customer data, including financial details and personal identifiers. A financial institution that implemented a robust data classification framework was able to segment customer information effectively, thereby enhancing the security of sensitive data and adhering to the principles of the GDPR.
By classifying data such as bank account numbers as ‘Confidential’, the institution ensured that this critical information received the highest level of protection. This approach not only organised sensitive information but also enabled better compliance with GDPR and enhanced overall data security.
Healthcare Industry
In the healthcare industry, managing protected health information (PHI) is paramount. A healthcare provider implemented a data classification strategy that enabled the effective handling of PHI, ensuring compliance with GDPR standards. To manage PHI, healthcare organisations implemented security measures such as access controls, encryption, and audit trails.
These practices ensured that patient data was managed securely and in accordance with GDPR, demonstrating the critical role of data classification in safeguarding health data.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Data Classification
Implementing data classification is not without its challenges. Organisations often struggle with managing large volumes of data, ensuring consistency and accuracy, and keeping up with evolving compliance requirements. To navigate these challenges, organisations must adopt a combination of data management practices, technology, policy development, and employee engagement.
Regularly reviewing technology infrastructure and adopting automated tools can help mitigate technological challenges. Effective data classification also supports Data Protection Impact Assessments, helping to identify and reduce risks.
Handling Large Volumes of Data
Handling large volumes of data can be a significant challenge due to high volume, unstructured data, system sprawl, and the variety of data types. Manual data classification is prone to errors and inconsistencies, rendering it impractical and inefficient when handling large datasets.
Organisations can utilise automated tools to enhance accuracy and efficiency, and identify and remove redundant, outdated, or trivial (ROT) data, thereby reducing the attack surface and storage costs.
Ensuring Consistency and Accuracy
Ensuring consistency and accuracy in data classification is crucial for maintaining compliance and protecting data. Automated scanning tools enhance the accuracy and efficiency of data classification, allowing organisations to maintain consistency across various data types.
Regular audits and updates are essential to ensure ongoing compliance and address emerging risks. Thorough documentation and effective communication of data classification policies help ensure that all members of the organisation are aligned and aware of classification standards.
Future Trends in Data Classification
As technology evolves, so do the trends in data classification. Emerging technologies like AI and machine learning are enhancing data classification processes by providing more nuanced and real-time categorisation, improving accuracy and efficiency. Evolving privacy regulations also necessitate adaptive strategies in data classification practices to keep pace with changes and maintain compliance.
Organisations must prioritise these adaptive strategies, enabling organisations to confront the challenges posed by advancements in technology and regulatory landscapes.
AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning technologies are revolutionising data classification by automating the process and providing more profound insights. The surge in data volume, velocity, and variety has led to the development of automated data classification systems, as manual classification has become inadequate. Machine learning algorithms can automatically classify data based on patterns, thereby significantly accelerating data processing.
Natural language processing (NLP) technologies are improving the understanding of data context for better classification. Using semantic and sentiment analysis techniques, AI provides deeper insights into data classification, enabling more precise categorisations. The integration of AI and machine learning facilitates real-time categorisation, enhancing the overall data classification process.
Evolving Privacy Regulations
Evolving data privacy regulations require organisations to adapt their data classification practices to remain compliant with legal standards. Organisations must develop flexible data classification strategies that can effectively accommodate new and changing privacy laws.
AI and machine learning technologies can significantly enhance data classification efficiency, enabling organisations to manage compliance under evolving privacy regulations better.
Summary
In conclusion, data classification is a vital practice for achieving and maintaining GDPR compliance. By organising and categorising data based on sensitivity and importance, organisations can protect personal data, enhance data security, and meet regulatory requirements. Implementing a comprehensive data classification policy, utilising automated tools, and conducting regular audits are essential steps for effective data classification.
As we look to the future, emerging technologies like AI and machine learning will continue to transform data classification processes, enabling organisations to stay ahead of evolving privacy regulations and maintain compliance. By prioritising data classification and integrating it with broader security measures, organisations can safeguard sensitive information, build trust with customers and partners, and ensure long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is data classification?
Data classification is the systematic organisation of data according to its sensitivity and significance, which is essential for implementing suitable security measures and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Why is data classification important for GDPR compliance?
Data classification is crucial for GDPR compliance, as it enables organisations to identify, protect, and manage personal and sensitive data effectively, thereby mitigating risks associated with data breaches and ensuring adherence to regulations.
What are the key elements of a data classification policy?
A robust data classification policy must clearly define goals, procedures, roles, responsibilities, and compliance requirements, while also ensuring involvement from key stakeholders and providing necessary training and communication. This comprehensive framework is essential for effective data governance.
How do automated tools enhance data classification?
Automated tools enhance data classification by leveraging machine learning algorithms to swiftly analyse large datasets, resulting in improved accuracy and efficiency in identifying sensitive information. This ultimately helps ensure better compliance with regulations such as the GDPR.
What are the future trends in data classification?
Future trends in data classification will be driven by the integration of AI and machine learning for improved real-time categorisation and accuracy, along with adaptive strategies addressing evolving privacy regulations. This shift will significantly enhance data management and compliance practices.