
PII vs PCI: Key Differences and Best Practices
Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and Payment Card Information (PCI) are two critical data types that require unique protection measures. PII covers personal identifiers, such as names, while PCI focuses on payment card details. This article will examine the differences between PII and PCI, their significance, and effective methods for securing them.
Key Takeaways
• Personally Identifiable Information (PII) encompasses any data that can identify an individual, while Payment Card Information (PCI) refers explicitly to sensitive data related to payment transactions.
• Compliance with regulatory frameworks such as GDPR for PII and PCI DSS for PCI data is essential for protecting sensitive information and preventing legal repercussions.
• Implementing best practices such as data encryption, access controls, and regular audits is critical for ensuring the security and integrity of both PII and PCI data.
Understanding PII and PCI
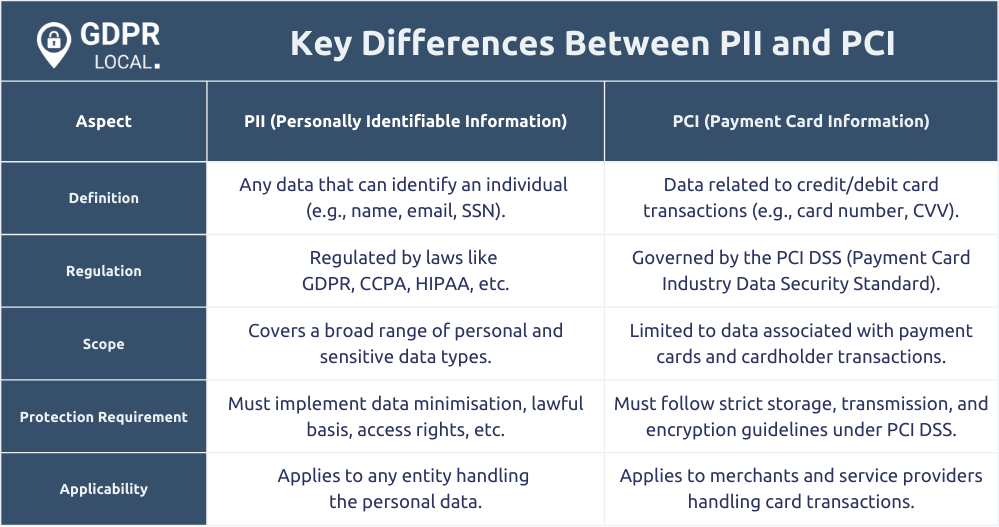
Understanding what constitutes Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and Payment Card Industry (PCI) data is crucial to protecting PII effectively. PII refers to any data that can be used to identify an individual, including names, addresses, and Social Security numbers.
On the other hand, PCI data, a subset of PII, includes sensitive cardholder information such as account numbers and security codes, primarily related to payment transactions.
What is PII?
Personally Identifiable Information (PII) is a broad category encompassing any data that can be used to identify an individual, including personal identifying information. This includes full names, social security numbers, email addresses, phone numbers, and home addresses. PII is a prime target for identity theft and fraud because it can reveal a person’s identity.
PII is typically categorised into two types: sensitive and non-sensitive. Sensitive PII, such as social security numbers and financial information, can cause significant harm if disclosed. Non-sensitive PII, like zip codes or dates of birth, may seem harmless on their own, but can become sensitive when combined with other personal information.
Distinguishing between sensitive and non-sensitive personally identifiable information (PII) is crucial for implementing effective data protection strategies. For example, an email address alone might not pose a significant risk, but when combined with financial data or IP addresses, it becomes sensitive personal data.
What is PCI?
Payment Card Information (PCI) refers to the data associated with payment cards. It includes all details associated with credit and debit card transactions, including payment card transaction details. This includes cardholder names, card numbers, expiration dates, security codes, and payment cards. The PCI Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) sets stringent guidelines to protect this data, ensuring the security of payment card transactions.
PCI data is highly sensitive due to its direct link to financial transactions. Elements such as Primary Account Numbers (PAN), CVV codes, and PIN codes are critical for processing payments and must be safeguarded to prevent fraud and identity theft.
PCI DSS compliance is of utmost importance. Adhering to these standards allows businesses to protect cardholder data, mitigate fraud risk, and foster customer trust.
Key Differences Between PII and PCI
While PII and PCI data are crucial for protecting personal information, they differ significantly in several ways, particularly in the context of PII versus PHI. The primary distinction lies in the nature of the data: PII pertains to personal identifiers, whereas PCI focuses specifically on payment-related information.
Recognising these differences is crucial for implementing appropriate security measures and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Data Types
PII includes a wide range of information, such as names, addresses, and other identifiers that can be used to trace an individual’s identity. This data becomes even more critical when combined with other information, making it easier for cybercriminals to commit identity theft and fraud.
PCI data concerns payment card information, including card numbers, expiration dates, and security codes. PCI data is used during payment card transactions to authorise and process payments, making its protection vital to preventing fraud in financial details.
Regulatory Frameworks
Various regulatory frameworks govern the protection of personally identifiable information (PII) and payment card information (PCI) data. For PII, regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) mandate stringent security standards to protect personal data from unauthorised access. Organisations must implement data security safeguards and breach notification systems under these laws.
On the other hand, PCI data is governed by the PCI Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), which outlines comprehensive security measures to protect cardholder information during payment card transactions. Compliance with the PCI DSS is crucial for preventing fraud and ensuring the security of payment card data.
Compliance Requirements
Compliance with data protection regulations is critical to prevent legal and financial penalties for mishandling PII and PCI data. Organisations must establish clear policies and procedures for handling PII to ensure effective management of sensitive data.
Regular risk evaluations and audits are crucial for identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring compliance with applicable laws and standards. Additionally, providing employees with compliance training is vital to ensure they understand the regulations and can effectively safeguard sensitive data.
Importance of Protecting PII and PCI
The importance of protecting PII and PCI data cannot be overstated. Security breaches involving this data can result in significant financial losses, legal repercussions, and severe damage to a business’s reputation. Protecting this information helps organisations prevent identity theft and financial fraud while maintaining customer trust.
Identity Theft Prevention
Protecting PII is crucial for reducing the risk of identity theft. Necessary security protocols, such as secure storage, transmission, and processing of PII, help maintain its confidentiality and integrity. Implementing robust security measures ensures that sensitive personal information remains protected from unauthorised access.
Effective identity theft prevention requires a multi-layered approach, including data encryption, access controls, and regular audits. These measures help organisations detect and prevent potential breaches, protect personal information, and reduce identity theft risk.
Financial Security
Securing PCI data is fundamental to preventing fraudulent transactions and ensuring customers’ financial security. Consumers are particularly concerned about the safety of their card information during transactions, making it essential for businesses to implement robust security measures focused on protecting cardholder data.
Effective PCI data security measures include encryption, access controls, and regular audits to identify and address vulnerabilities. Maintaining high security standards allows organisations to protect cardholder data and prevent financial fraud.
Customer Trust and Reputation
Data breaches can significantly harm customer trust and a business’s reputation. Ensuring robust protection of customer data demonstrates a commitment to security and can positively influence overall business reputation.
Maintaining customer trust requires consistent and transparent communication about data protection practices. Implementing and adhering to stringent security measures builds and maintains customer trust, enhancing overall business reputation while protecting customer data.
Best Practices for Securing PII and PCI Data
Implementing best practices for data protection is essential for safeguarding PII and PCI data in an increasingly digital world. A multi-layered approach that combines sound business processes with robust technology controls can significantly enhance data security for the data owner.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is critical to data security, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential during storage and transmission. Protecting data helps encrypt data from unauthorised access and breaches, making it an essential practice for safeguarding sensitive information.
Implementing robust encryption practices involves encrypting data both at rest and in transit. This prevents interception and ensures that sensitive information remains secure as it is transmitted between systems.
Access Controls
Access controls are vital for limiting who can access sensitive PII and PCI data. Role-based access control ensures that only authorised personnel can interact with this information, significantly enhancing data security.
Restricting unauthorised access helps organisations prevent data breaches and maintain the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information. Robust access controls are a fundamental aspect of any comprehensive data protection strategy.
Regular Audits
Regular audits are essential for identifying security weaknesses and ensuring ongoing regulatory compliance. Regular risk assessments help businesses detect vulnerabilities and enhance their defences against potential threats.
Audits should result in a report that outlines findings and provides suggestions for improvement. This helps organisations refine their compliance policies and address any identified flaws. Prioritising regular audits ensures the effectiveness of data protection strategies.
Real-World Examples of PII and PCI Breaches
Studying real-world examples of PII and PCI breaches helps us understand organisations’ vulnerabilities and the consequences of data breaches.
High-Profile PII Breach
In 2024, Hathway’s data breach exposed the sensitive KYC details of 4 million users, raising significant concerns about identity theft. Additionally, the National Public Data breach exposed 2.9 billion records, affecting 170 million individuals and highlighting the importance of secure access controls.
These breaches significantly increased the risk of identity theft and financial fraud for millions of affected individuals. The incidents underscore the necessity of implementing stringent access controls to prevent unauthorised data breaches.
Major PCI Breach
In 2024, a significant PCI breach was reported involving a major retailer. Hackers accessed the credit card data of over 100,000 customers through a phishing scheme. Another notable incident involved the Bank of America ransomware attack, which exposed over 57,000 customers’ credit card information, severely impacting customer trust and financial security.
These breaches underscore the urgent need for security measures to safeguard payment card data and prevent financial fraud. Organisations must prioritise PCI DSS compliance to protect cardholder information during payment card transactions.
How to Respond to a Data Breach
Responding effectively to a data breach is crucial for minimising its impact. Swift action to identify, contain, and mitigate the violation can significantly reduce financial and reputational damage.
This section will guide you on how to respond effectively to data breaches.
Incident Response Plan
A well-defined incident response plan is crucial for effectively managing data breaches. It should outline procedures for reporting incidents, the roles of team members, and steps to establish a timeline of the breach. An effective incident response plan helps organisations minimise damage and recover quickly.
Implementing these elements in an incident response plan enables organisations to respond efficiently and effectively to data breaches, thereby mitigating their impact and preventing future incidents through the use of intrusion detection systems.
Notification Requirements
Organisations are legally obliged to notify affected individuals promptly if a data breach poses a high risk to them. Adhering to specific timelines and formats for these notifications ensures compliance with data privacy laws and helps maintain customer trust.
Remediation Efforts
Post-breach remediation efforts are critical for mitigating the effects of a data breach. Businesses must act swiftly to execute their incident response plan, which should outline specific roles, responsibilities, and procedures for efficiently handling the breach.
Implementing effective security measures for data protection strategies, such as data encryption and access controls, is crucial for preventing future breaches. Regular audits should be conducted to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with data protection standards.
Summary
Understanding the differences between PII and PCI, their respective regulatory frameworks, and compliance requirements is essential for protecting sensitive data. By implementing best practices for data security, organisations can prevent breaches, safeguard customer information, and maintain trust. The key to robust data protection lies in a multi-layered approach that combines sound business processes with advanced technological controls.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between PII and PCI?
The primary difference between PII and PCI is that PII refers to any data that can be used to identify an individual directly or indirectly. At the same time, PCI specifically pertains to sensitive payment card details. Understanding this distinction is crucial for adequate data protection and compliance.
Why is it essential to protect PII and PCI data?
Protecting PII and PCI data is crucial to prevent identity theft and financial fraud, which can result in significant economic losses and damage a business’s reputation. Ensuring the security of this information also maintains customer trust, a vital component for any successful business.
What are some regulatory frameworks governing PII and PCI data?
Regulatory frameworks governing Personally Identifiable Information (PII) include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). The governing standard for the payment card industry (PCI) data is the PCI Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
What are the best practices for securing PII and PCI data?
To secure PII and PCI data, it is essential to implement data encryption, access controls, regular audits, intrusion detection systems, and a defined incident response plan. Adhering to these practices significantly enhances data protection and mitigates risks.
How should an organisation respond to a data breach?
An organisation must act swiftly to identify and contain the data breach by promptly implementing an incident response plan, notifying affected individuals, and enhancing security measures. These actions are crucial for mitigating damage and protecting sensitive information.