
Global Data Protection Regulation: How GDPR Sets the International Standard
Updated, June 2025
We’re in the midst of a data protection revolution, and the global data protection regulation known as GDPR is leading the charge. As businesses and organisations around the world grapple with the ever-growing importance of data privacy, GDPR has emerged as the gold standard for safeguarding personal information. Our team of experts is here to guide you through the ins and outs of this game-changing regulation and its far-reaching effects on the international stage.
Key Takeaways
GDPR Sets the Global Standard for Data Protection
With principles like data protection by design, enhanced individual rights, and accountability, the GDPR has influenced legislation worldwide, from Brazil’s LGPD to China’s PIPL, becoming the benchmark for privacy compliance.
Extraterritorial Scope and Transfer Rules Extend GDPR’s Reach
GDPR applies to any organisation handling EU residents’ data, regardless of location, and places strict controls on cross-border data transfers, compelling global businesses to align their practices with EU standards.
Compliance Requires Strategic Operational Changes
Key challenges include data mapping, managing consent, conducting DPIAs, and responding to breaches within 72 hours. Automated tools, dedicated teams, and structured governance frameworks are crucial for efficiently meeting GDPR obligations.
Key Principles of GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets the international standard for data protection with its core principles. These principles form the foundation of the regulation and guide organizations in their data processing activities. We’ll explore the key principles that make GDPR a good framework for safeguarding personal information.
Data protection by design and default
We believe that data protection should be an integral part of any processing activity from the very beginning. The GDPR requires us to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to ensure data protection principles are effectively put into practice. This concept, known as “data protection by design and by default,” is now a legal requirement under the regulation.
To comply with this principle, we need to consider data protection issues upfront in everything we do. This approach helps us ensure that we meet the GDPR’s fundamental requirements and demonstrates our commitment to accountability. By integrating data protection concerns into every aspect of our processing activities, we can better safeguard individuals’ rights and freedoms.
Lawful basis for processing
Under the GDPR, we must have a valid lawful basis to process personal data. There are six lawful bases available, and we need to determine which one is most appropriate for our specific purpose and relationship with the individual. These bases include consent, contract, legal obligation, vital interests, public task, and legitimate interests.
It’s crucial for us to establish our lawful basis before we begin processing and to document it clearly. We should also be cautious about changing our lawful basis later without good reason, as this can have significant implications for compliance.
Data subject rights
The GDPR grants individuals several rights concerning their personal data. As data controllers, we have to respect and facilitate these rights. Some of the key data subject rights include:
1. Right to be informed: We must provide clear and concise information about how we collect and use personal data.
2. Right of access: Individuals can request access to their personal data and receive a copy of the information we hold about them.
3. Right to rectification: We need to correct inaccurate or incomplete personal data upon request.
4. Right to erasure: Also known as the “right to be forgotten,” individuals can ask us to delete their personal data in certain circumstances.
5. Right to data portability: We must provide personal data in a structured, commonly used, and machine-readable format when requested.
6. Right to object: Individuals can object to the processing of their personal data in specific situations.
These rights empower individuals and give them more control over their personal information.
Accountability and governance
The principle of accountability is a cornerstone of the GDPR. It requires us to take responsibility for our data processing activities and to demonstrate compliance with the regulation’s principles. This means we need to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to ensure and document our compliance.
To meet this requirement, we should consider the following:
- 1. Implementing comprehensive privacy governance structures
- 2. Conducting data protection impact assessments (DPIAs)
- 3. Maintaining records of processing activities
- 4. Appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO) when required
- 5. Developing internal guidelines and policies for data protection
- 6. Subscribing to industry codes of conduct or certification mechanisms
By embracing accountability, we can create a culture of data protection within our organization and build trust with our stakeholders.
Global Impact of GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has had a profound effect on data protection practices worldwide. Its influence extends far beyond the borders of the European Union, shaping global standards for privacy and data security.
Influence on data protection laws worldwide
We’ve seen a significant shift in the global privacy landscape since the GDPR came into effect. The regulation has sparked a wave of new data protection laws and updates to existing ones across the globe. This trend, often referred to as the ‘Brussels effect,’ has led to many countries mirroring GDPR principles in their own legislation.
For instance, Brazil’s Lei Geral de Proteçao de Dados, which came into force in 2020, was modeled directly after the GDPR. Similarly, China introduced its Personal Information Protection Law in 2021, drawing inspiration from the EU’s regulation. Japan, too, has updated its Act on the Protection of Personal Information several times to align with GDPR standards. The impact of GDPR has reached even further, influencing legislation in countries like India, which recently enacted its Digital Personal Data Protection Act in 2023. In the United States, while there’s no federal data protection law, several states have introduced their own regulations, such as California’s Consumer Privacy Act and Virginia’s Consumer Privacy Act.
This global adoption of GDPR-inspired laws has led to a remarkable increase in data protection coverage worldwide. According to recent statistics, 137 countries now have national data privacy laws, covering 79.3% of the world’s population.
Extraterritorial scope
One of the most significant aspects of the GDPR is its extraterritorial reach. The regulation applies not only to organizations based in the EU but also to those outside the EU that offer goods or services to EU residents or monitor their behavior.
This extraterritorial scope has had a considerable impact on multinational companies, particularly those in industries like technology, telecommunications, finance, hospitality, and logistics. These companies have had to review and update their privacy policies and practices to comply with GDPR, even if they’re not based in the EU.
Many businesses operating globally out of regions like Hong Kong have chosen to adopt GDPR standards for processing data of non-EU subjects as well. This is because the GDPR is widely recognized as a prominent benchmark for data protection, and companies often opt to implement its principles consistently across all regions to demonstrate their commitment to data privacy.
Data transfer restrictions
To facilitate these transfers while maintaining data protection standards, the GDPR provides several mechanisms. These include adequacy decisions, where the European Commission formally confirms that a non-EEA country offers an adequate level of data protection, and appropriate safeguards such as Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) or Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs).
The GDPR has also introduced strict rules regarding the transfer of personal data outside the European Economic Area (EEA). These restrictions have a significant impact on international trade and cooperation, as many businesses need to share personal data with partners or suppliers based outside the EEA.
The impact of these restrictions has been felt globally, with many countries and organizations having to adapt their data handling practices to ensure compliance. For instance, Japan became the first Asian country to be granted adequacy status by the European Commission in 2019, following its issuance of supplementary legislation to enhance its data protection. In conclusion, the GDPR has set a new global standard for data protection, influencing legislation and business practices worldwide. Its extraterritorial scope and data transfer restrictions have compelled organizations globally to reassess and improve their data protection measures, leading to enhanced privacy rights for individuals far beyond the borders of the EU.
Compliance Challenges and Solutions
We’ve found that complying with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) presents significant challenges for many organizations. Our research shows that as many as half of companies feel somewhat unprepared for GDPR compliance, often relying on temporary controls and manual processes until more permanent solutions can be implemented. This highlights the complexity of adapting to this new regulatory landscape.
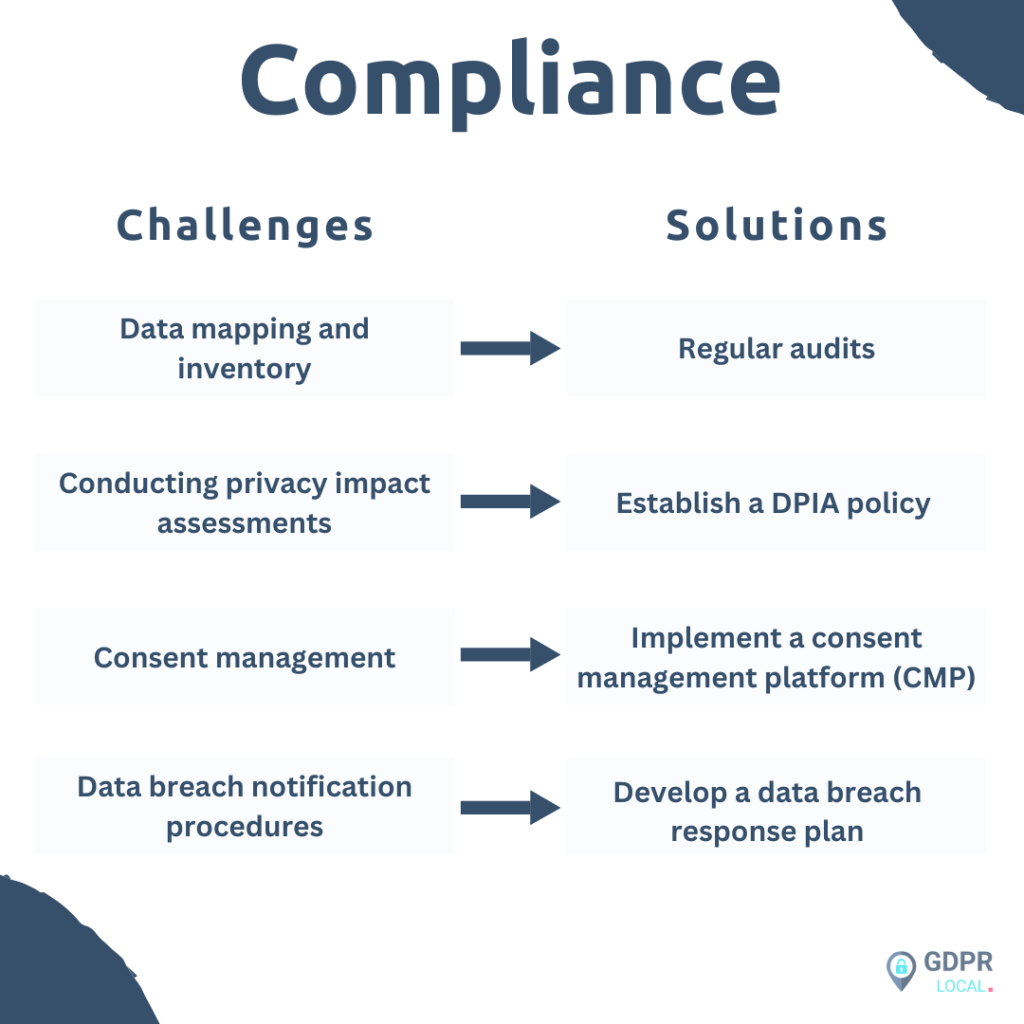
One of the primary hurdles we face is data mapping and inventory. To comply with GDPR requirements, we must identify and track the flow of personal data within our organization. This task can be exhausting, especially when dealing with data from various sources like mobile applications, websites, and third parties. The dynamic nature of data environments further complicates this process, making it difficult to maintain an up-to-date inventory.
To address this challenge, we recommend conducting regular audits to discover new data sources and implementing automated data mapping tools. It’s crucial to have a specialized team dedicated to this task, ensuring that our organization maintains a comprehensive understanding of its data landscape.
Another significant challenge is conducting privacy impact assessments. The GDPR mandates that we perform Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) for high-risk data processing activities. This process involves identifying and assessing risks to data subjects’ rights and freedoms, which requires dedicated time, expertise, and effort.
To overcome this hurdle, we suggest establishing a DPIA policy and allocating resources to a team with diverse backgrounds, including technical, legal, and cybersecurity experts. Utilizing automated tools and checklists can also streamline the assessment process.
Consent management poses another critical challenge. The GDPR requires us to have a streamlined process for fulfilling data subject requests promptly, ensuring that individuals’ rights are protected and can be properly exercised. This can be time-consuming, especially when dealing with a large number of requests.
To address this, we recommend implementing a consent management platform (CMP) that automates the consent process and stays up-to-date with regulation changes. This approach not only saves time and resources but also helps build trust with customers by demonstrating our commitment to data privacy. Lastly, data breach notification procedures present a significant compliance challenge. The GDPR mandates that we notify relevant authorities of a personal data breach within 72 hours of becoming aware of it. Failure to meet this deadline can result in substantial penalties.
To ensure compliance, we advise developing a comprehensive data breach response plan. This plan should outline roles and responsibilities, include steps for responding to and documenting breaches, and be regularly reviewed and updated. Implementing continuous cybersecurity monitoring solutions can also help us maintain ongoing surveillance for potential data breaches.
In conclusion, while GDPR compliance presents numerous challenges, we believe that by implementing these solutions and maintaining a proactive approach to data protection, we can operate the regulation effectively.
Conclusion
The GDPR has truly shaken up the world of data protection, setting a new standard that’s rippling across the globe. Its key principles, like data protection by design and beefed-up rights for individuals, are reshaping how businesses handle personal information. We’ve seen countries from Brazil to China taking cues from the GDPR, showing just how far-reaching its impact has been.
While getting on board with GDPR can be tough, it’s a challenge worth tackling. By diving into data mapping, nailing down consent management, and staying on top of breach notifications, companies can not only stay in line with the rules but also build trust with their customers. In the end, embracing GDPR isn’t just about dodging fines, it’s about showing we care about people’s privacy in our increasingly connected world.
FAQs
1. Does the GDPR apply to companies outside the EU?
Yes. The GDPR applies to any organisation, regardless of location, that offers goods or services to EU residents or monitors their behaviour—this is known as its extraterritorial scope.
2. What are the biggest challenges businesses face with GDPR compliance?
Major challenges include creating accurate data maps, managing consent across systems, conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs), and responding to data breaches within 72 hours. Each requires a proactive, structured approach.
3. How has the GDPR influenced global privacy laws?
The GDPR has inspired similar laws globally, including Brazil’s LGPD, China’s PIPL, and updated frameworks in Japan and India. Many organisations adopt GDPR principles globally to streamline operations and demonstrate a high standard of data protection.