
How to Implement the New AI Law in Your Company
The implementation of the AI Act marks a significant stride towards responsible and fair use of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies within the European Union (EU) market. This comprehensive set of rules, proposed by the European Commission in April 2021, targets a broad spectrum of stakeholders in the AI domain, including startups, healthcare entities, and beyond, whether operating within or aiming to enter the EU market. Catering to the urgent need for a risk-based regulatory approach, the AI Act is designed to ensure that AI applications foster trust amongst Europeans by addressing specific risks and outrightly banning AI practices considered to pose unacceptable dangers. Given the surge in AI adoption across sectors, with 90% of leading enterprises globally leveraging AI for enhanced analytics and productivity, the significance of adhering to the AI Act cannot be understated for startups, healthcare ventures, and other entities engaging with artificial intelligence.
As these regulations begin to reshape the landscape of AI and data protection, understanding and implementing the AI law in your company becomes paramount. This article aims to guide startups, healthcare providers, and all entities involved with artificial intelligence through the nuances of assessing compliance requirements and deploying effective AI data protection measures. With a spotlight on addressing the challenges and carving out viable solutions, this narrative serves as a roadmap for harnessing the potential of AI within the legal confines established by the AI law.
Understanding New AI Data Protection Regulations
The European Union’s AI Act is a pioneering regulation, establishing a legal framework for AI use across member states. It categorizes AI systems into various risk levels, from minimal to unacceptable, tailoring regulatory requirements accordingly to ensure safety and transparency. High-risk categories include AI applications in critical infrastructure and those integrated into product safety under EU legislation, necessitating stringent compliance measures.
Risk Categories and Prohibitions
Unacceptable Risk: Certain AI practices, such as social scoring and real-time biometric identification, are completely prohibited due to their potential for abuse and significant privacy infringements.
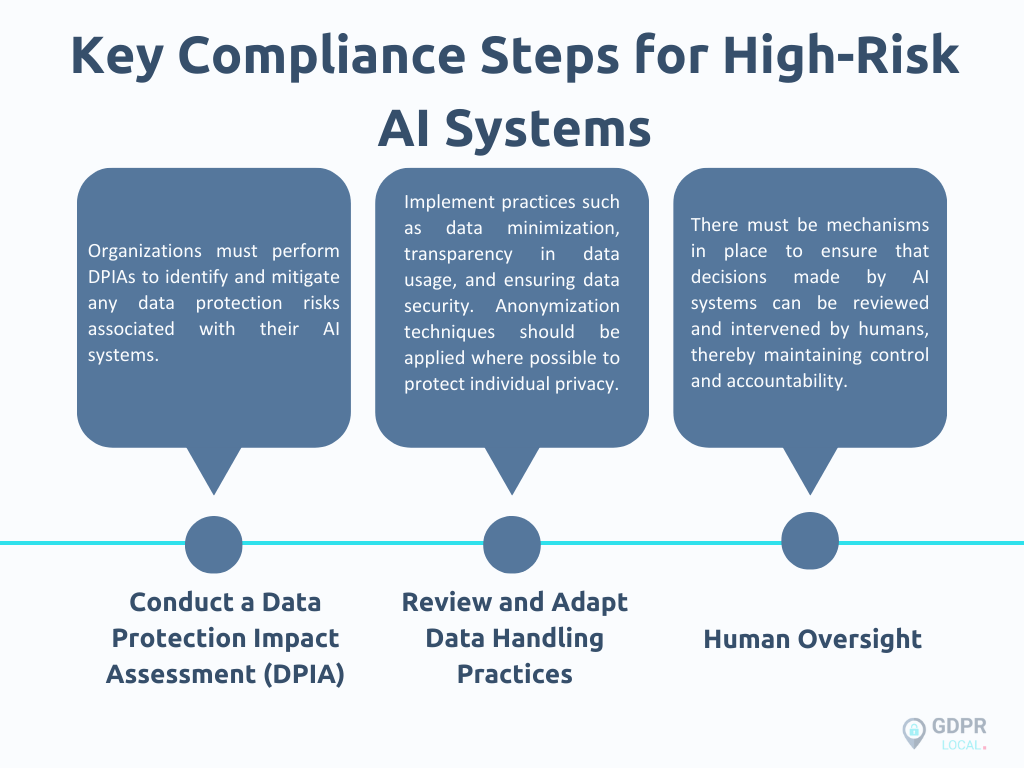
High-Risk Systems: These systems are subject to rigorous requirements, including thorough risk assessments, adherence to strict data governance standards, and ensuring clear transparency and human oversight in decision-making processes.
Compliance and Enforcement
Companies operating within the EU must ensure their AI systems, regardless of the development location, comply with the AI law. This includes conducting detailed risk assessments and implementing necessary measures to protect user data and privacy. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties, including fines up to 6% of global annual revenue, emphasizing the importance of adherence. For businesses outside the EU, compliance is equally crucial to maintain market access within the region.
For guidance on navigating regulations, we offer support to help companies integrate requirements into their operations. Visit our website – GDPRlocal for expert advice and assistance in ensuring your AI systems are compliant with the latest EU standards.
Assessing Compliance Requirements
To effectively assess compliance requirements under the new AI law, companies must undertake a detailed evaluation of their AI systems, especially those classified as high-risk. This involves several key steps to ensure that all aspects of AI deployment align with stringent legal standards.
Key Compliance Steps for High-Risk AI Systems
Transparency and Documentation
Organizations are required to maintain comprehensive documentation of AI systems’ data handling and decision-making processes. This includes:
– Clear records of data processing activities;
– Justification of the algorithms used;
– Measures taken to ensure fairness and prevent biases.
Legal Compliance and Risk Management
Identifying Legal Basis for Data Processing: Companies must clearly identify and document the legal basis for processing personal data using AI, ensuring adherence to privacy principles.
Regular Audits and Updates: Regular audits should be conducted to ensure ongoing compliance with AI law. This includes reviewing AI systems for any potential biases and updating systems in accordance with current laws and technological advancements.
By partnering with us, companies can ensure that their AI implementations are both effective and compliant with the latest EU standards. Visit GDPRlocal for more information on how to seamlessly integrate these compliance measures into your operational framework.
Strategies for Implementing AI Data Protection Measures
Ethical and Transparent AI Practices
1. Transparency and Explainability: It is crucial to ensure that customers understand how AI-based platforms utilize their personal data and the implications of AI-generated outcomes. This fosters trust and ensures compliance with data protection laws.
2. Ethical Testing: Integrating ethical testing within AI development processes ensures that decisions made by AI systems are fair, explainable, and free from biases. This step is essential to uphold ethical standards and maintain public trust in AI technologies.
3. Handling Data Privacy Requests: Implement procedures for addressing data privacy requests promptly, including the right to be forgotten and the right to human intervention in AI-driven decisions. This compliance is not only a legal requirement but also a best practice in customer relations management.
Data Minimization and Security
1. De-identify Personal Data: Employ techniques such as aggregation, pseudonymization, and anonymization to safeguard customer identities. These methods help minimize the risks associated with data breaches and privacy violations.
2. Minimize Personal Data Use: Adhere to the principle of data minimization by collecting only the necessary data required for processing. This approach not only complies with legal standards but also reduces the potential for data misuse.
3. AI-Specific Data Threats: Conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) to understand data flows and the algorithms that support them, ensuring transparency in how decisions are made.
Continuous Improvement and Accountability
1. Risk Assessment and Management: Regularly conduct thorough risk assessments to identify and mitigate potential ethical, legal, and societal risks associated with AI systems. This proactive approach helps in designing strategies that prevent issues before they arise.
2. Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation: Establish a routine for ongoing monitoring and evaluation of AI systems to ensure they adhere to ethical guidelines and adjust operations as necessary. This continuous oversight helps in maintaining compliance and operational integrity.
3. AI Governance and Training: Develop an AI governance program that remains relevant and meets business needs. Implement ongoing training to advance AI literacy across the organization, promoting a culture of responsible AI usage.
By incorporating these strategies, businesses can effectively implement AI data protection measures, ensuring compliance with the new AI law. For further guidance and support, visit our website – GDPRlocal.
Challenges and Solutions in AI Data Protection
Data Collection and Privacy Concerns
Private Data Collection Risks: AI systems necessitate substantial datasets, heightening the risk of tracking private information.
◦ Solution: Implement rigorous management and monitoring protocols. Establish a comprehensive inventory of AI systems and set up monitoring procedures for early detection of ethical issues.
Repurposing of Data: The potential for discovering new uses for collected data can lead to excessive data collection by AI technologies.
◦ Solution: Formulate teams dedicated to compliance, fairness, and system governance to manually review and ensure AI systems remain unbiased and trustworthy.
Constant Surveillance: AI-powered digital assistants that enable persistent observation may infringe on individual privacy.
◦ Solution: Keep abreast of regulatory developments to circumvent fines and penalties, ensuring that surveillance practices comply with legal standards.
Addressing Re-identification and Discrimination
Re-identification Attacks: AI software tracking behavioral patterns across devices can lead to easy identification of users.
◦ Solution: Utilize robust data governance tools to maintain control over data usage and ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
Data-Based Discrimination: AI algorithms may replicate existing biases, leading to misclassification and unfair judgment of certain groups.
◦ Solution: Employ data governance tools strategically to manage data effectively and ensure compliance with laws, thereby mitigating bias.
Enhancing Transparency and Security
Lack of Transparency: The ‘black box’ nature of AI systems often makes it challenging to understand their decision-making processes.
◦ Solution: Enhance transparency and explainability. Ensure that users can comprehend what data is utilized and how it is processed.
Data Breaches: The vast data repositories required by AI systems make them prime targets for cyberattacks.
◦ Solution: Solution: Secure data storage and transmission by employing encryption and other security measures to protect data integrity and confidentiality.
For further assistance in integrating these AI data protection strategies into your operations, consider partnering with ус for expert guidance and support. Visit GDPRlocal for more information on how to effectively manage AI law within your organization.
Conclusion
By delving into the intricacies of the AI Act, from understanding its broad reach over various risk categories to the actionable steps for achieving compliance and enforcing data protection measures, we’ve laid a roadmap for businesses. This journey underscores the importance of adherence to legal frameworks in enhancing AI’s ethical use.
As businesses strive to align with these stringent yet crucial regulations, the path forward involves continuous engagement with AI’s legal and ethical dimensions. Recognizing the broader implications of AI’s integration into our digital society will be pivotal in advancing a responsible and transparent AI ecosystem. For personalized guidance on the AI Act’s requirements and integrating its principles, contact our team to help with compliance.
Embracing these regulations not only safeguards consumer rights but also positions companies as leaders in the responsible adoption of AI technologies.
FAQs
What are the steps to introduce AI into a company?
To introduce AI in a business, begin by identifying areas within the company that could gain from AI. Evaluate various AI technologies and service providers to find the best fit. Develop a plan for AI rollout, ensure quality data availability, and assemble a dedicated team for implementation.
What is the process for setting up an AI system in a business?
Implementing an AI system involves several key steps:
– Define clear objectives for what you hope to achieve with AI.
– Assess your company’s readiness and the resources you have available.
– Educate yourself and your team on AI capabilities and limitations.
– Identify specific use cases where AI can be applied.
– Develop a strategic approach to data management.
– Select appropriate AI tools and technologies.
– Develop and train AI models to meet your needs and be compliant with the AI law.
– Conduct pilot tests and evaluate the results to refine the system.
How is AI utilized in the legal sector?
In the legal field, AI is primarily used to enhance the efficiency of document review processes. AI-powered due diligence tools can quickly extract and compile documents that contain specific clauses or information needed for legal reviews. Additionally, these tools are also capable of detecting variations and modifications in documents, which is crucial for thorough legal analysis.
What is AI, and what does its implementation involve?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) operates by processing vast amounts of data through advanced algorithms in a rapid, iterative manner. This process enables the AI to learn autonomously from the patterns and features in the data. Implementing AI involves setting up systems to analyze data and adapt to new inputs without explicit programming for each task.
References
[1] – https://legalnodes.com/article/eu-ai-act-overview
[2] – https://www.bdo.co.uk/en-gb/insights/advisory/risk-and-advisory-services/navigating-the-eu-artificial-intelligence-(ai)-act-implications-and-strategies-for-uk-businesses
[3] – https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/regulatory-framework-ai
[4] – https://bmmagazine.co.uk/tech/business-best-practice-preparing-for-ai-regulation/
[5] – https://hbr.org/2024/02/the-eus-ai-act-and-how-companies-can-achieve-compliance
[6] – https://www2.deloitte.com/uk/en/blog/emea-centre-for-regulatory-strategy/2024/the-uks-framework-for-ai-regulation.html
[7] – https://www.europarl.europa.eu/topics/en/article/20230601STO93804/eu-ai-act-first-regulation-on-artificial-intelligence
[8] – https://www.reuters.com/legal/legalindustry/seeking-synergy-between-ai-privacy-regulations-2023-11-17/
[9] – https://www.allenovery.com/en-gb/global/blogs/data-hub/your-2023-wrapped-uk-ai-and-data-protection-edition
[10] – https://logic2020.com/insight/ai-data-privacy-strategies/
[11] – https://www.nele.ai/en/blog/data-protection-compliant-ki-use
[12] – https://shepwedd.com/knowledge/artificial-intelligence-focus-how-avoid-data-protection-risks-when-using-ai
[13] – https://www.grcworldforums.com/privacy-and-technology/where-do-businesses-stand-on-data-privacy-and-ai/9252.article
[14] – https://www.lexisnexis.com/community/insights/legal/b/thought-leadership/posts/for-in-house-counsel-5-essential-tips-for-implementing-ai-in-the-workplace
[15] – https://www.globallegalpost.com/news/contracting-for-ai-technologies-top-five-best-practices-1889322053
[16] – https://legalvision.co.uk/regulatory-compliance/lawfully-use-artificial-intelligence/
[17] – https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/strategies-implementing-responsible-ai-business-operations-boardsi-wuldc
[18] – https://iapp.org/news/a/five-compliance-best-practices-for-a-successful-ai-governance-program/
[19] – https://www.cookielawinfo.com/data-privacy-and-ai-governance/
[20] – https://www.itmagination.com/blog/ai-solutions-and-privacy-overcoming-common-challenges-committing-to-responsible-ai
[21] – https://www.thedigitalspeaker.com/privacy-age-ai-risks-challenges-solutions/
[22] – https://www.informationpolicycentre.com/uploads/5/7/1/0/57104281/cipl_second_report_-_artificial_intelligence_and_data_protection_-_hard_issues_and_practical_solutions__27_february_2020_.pdf
[23] – https://www.isaca.org/resources/news-and-trends/newsletters/atisaca/2021/volume-32/challenges-of-ai-and-data-privacy-and-how-to-solve-them