
Mastering GDPR Digital Marketing: Strategies for Compliance
To comply with GDPR in digital marketing, you need to understand data protection rules and implement key practices related to GDPR digital marketing. This guide covers everything from legal bases for processing data to obtaining valid consent and managing data breaches.
Key Takeaways
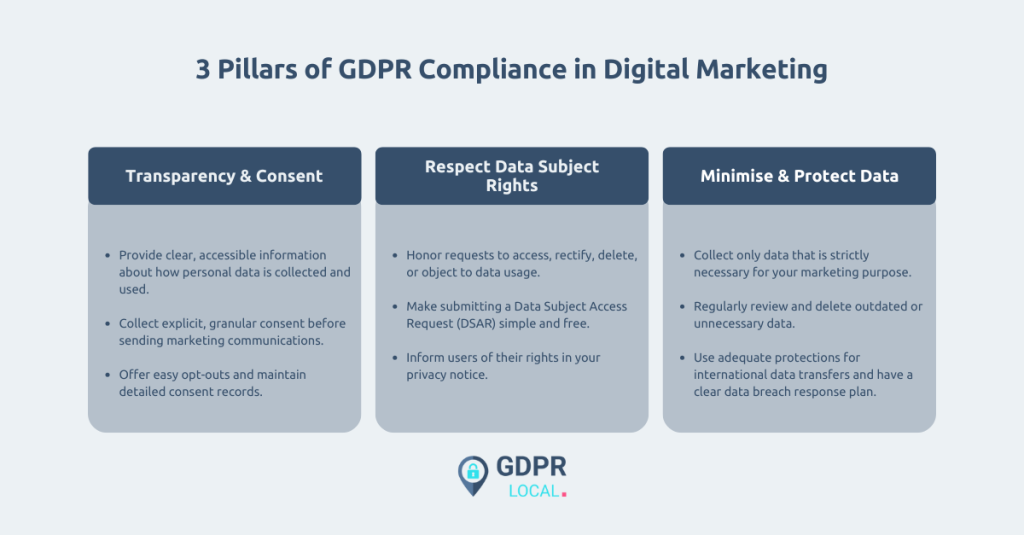
• GDPR mandates clear transparency in data-handling practices, affecting all businesses interacting with EU residents, irrespective of location, to avoid substantial fines.
• Consent and legitimate interests are the primary legal bases for processing personal data in marketing, requiring marketers to ensure clear communication and documentation of these processes.
• Marketers must respect data subject rights and implement effective data retention policies, ensuring only necessary personal data is collected and maintained to comply with GDPR.
Understanding GDPR and Its Impact on Digital Marketing
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has transformed digital marketing by enhancing consumer rights over personal data. This regulation mandates that businesses should provide clear and concise information regarding their data-handling practices. Digital marketers must adopt more responsible and transparent practices when collecting personal data. The aim is to protect individual rights and ensure data is used fairly and legally.
One of the most significant aspects of GDPR is its global reach. Any business with customers in the European Union (EU) must comply with GDPR, regardless of location. This means that even if your company is based outside the EU, if you are processing personal data of EU residents, you are subject to these regulations. The stakes are high, as non-compliance can result in substantial fines and damage your reputation.
Digital marketers must understand the implications of GDPR. Compliance is mandatory and requires a thorough understanding of the regulation’s requirements. All data practices must be legal, fair, and transparent. This approach helps marketers build trust with their audience and craft more effective, compliant marketing strategies.
Legal Bases for Processing Personal Data in Marketing
Digital marketers must grasp the legal basis for processing personal data under GDPR. This understanding is crucial for ensuring compliance with GDPR requirements. The two primary legal bases for processing personal data in marketing are consent and legitimate interests.
Consent must be explicit and specific and obtained for the intended purpose of data processing, such as marketing activities. This means that individuals must be fully informed about why their data is being collected and how it will be used.
On the other hand, legitimate interests can also be used as a legal basis, provided that the processing is necessary and justified for the marketing objectives. However, it is essential to balance these interests against the rights and freedoms of the data subjects.
Data controllers must document the lawful basis before starting any data processing to ensure compliance with GDPR. This documentation should be included in privacy notices, informing individuals about the lawful basis for processing their data.
Additionally, data subjects can object to personal data processing for marketing purposes at any time, free of charge. Ensuring transparency and respecting these rights is key to maintaining trust and compliance. They also need to process data in a manner that aligns with these principles.
Obtaining Valid Consent for Marketing Purposes
Securing valid consent from individuals before any marketing activity is crucial for GDPR compliance. Consent must be freely given, unambiguous, and transparent, aligning with GDPR requirements. Individuals must provide granular consent, agreeing to specific types of data processing under GDPR. For example, a customer might consent to receive email marketing but not to have their data shared with third parties.
Organisations are responsible for informing customers about why their data is being collected and how it will be used. This information should be presented in a clear and easily understandable manner. Consent must also be recorded to make it easy for individuals to understand and review their consent history. This helps demonstrate compliance if regulatory bodies ever question it.
Effective consent management involves providing opt-out options and a communication preferences page. The unsubscribe route must be simple and straightforward, allowing individuals to withdraw their consent easily. This process ensures that organisations respect individuals’ wishes when they withdraw their consent for marketing communications. Implementing these practices helps marketers maintain compliance and build audience trust.
Data Subject Rights and Responsibilities
The General Data Protection Regulation grants users several rights over their personal data, including the right to be informed, the right to access, the right to rectification, the right to erasure, and the right to object to processing. These rights empower individuals to have greater control over their data access and how organisations use it.
Under GDPR, data subjects can access their personal data at any time. They can request a copy of their data, request corrections, or even request the erasure of their data. The ‘right to be forgotten’ allows individuals to request the deletion of their personal data under certain circumstances. Marketers must ensure that data subjects can easily access their data. Options to correct, delete, or object to data processing should also be provided.
To comply with GDPR, marketers must offer an easily accessible way for data subjects to submit their data subject access requests (DSARs). Upon receiving a DSAR, marketers must provide a copy of all personal data they hold about the person, including consent history.
Failure to comply with data subject requests can lead to regulatory scrutiny and potential penalties. Marketing teams must inform data subjects about their rights regarding data processing through privacy notices.
Data Minimisation and Relevance in Marketing
The principle of data minimisation under GDPR states that personal data collected should be adequate, relevant, and limited to what is necessary for the intended marketing purpose. This means that marketers should only collect the data they need and avoid gathering unnecessary personal details that do not relate to their marketing goals. Collecting more personal data than required can lead to unlawful processing.
Marketers must avoid collecting customer data based on assumptions of future usefulness, focusing instead on current necessity. Organisations should periodically review their data to ensure collecting data for marketing purposes and deleting any unnecessary information remains necessary.
Adhering to the data minimisation principle reduces the risk of data breaches and ensures GDPR compliance.
Email Marketing Compliance
Email marketing managers must comply with GDPR to ensure valid marketing practices. Explicit consent is required for sending marketing emails to new prospects, while existing customers can receive emails without prior consent if a legitimate interest is established. To ensure compliance, a double opt-in process involving a confirmation link in an email is recommended for new prospects.
To comply with GDPR, all marketing emails must include an unsubscribe option. This ensures that recipients can easily opt out of receiving future communications, respecting their preferences and maintaining compliance. A legitimate interest assessment (LIA) for existing customers is also recommended to validate email marketing practices. This assessment helps balance the marketer’s interests with the rights and freedoms of the individuals.
Following these practices ensures GDPR compliance and builds audience trust for email marketers. This not only helps in avoiding penalties but also enhances the effectiveness of email marketing efforts.
Managing Data Breaches in Marketing
Data breaches are a significant concern under the General Data Protection Regulation, and managing them effectively is crucial for maintaining trust and compliance. When a data breach occurs, it is crucial to notify affected parties promptly and establish a clear timeline for publishing a notice post-breach. Effective communication during a data breach helps maintain transparency and trust with customers.
Preparing communication templates in advance can streamline the response process during a data breach. These templates should include key information that needs to be communicated to the affected individuals, such as the nature of the breach, the data involved, and the steps to mitigate the impact. Having these templates ready allows organisations to respond quickly and effectively, minimising potential damage and ensuring GDPR compliance.
Data Retention and Deletion Policies
Effective data retention policies are important for mitigating data breach risks and ensuring operational efficiency. Retention policies define the duration for storing personal data and the timing for its deletion or anonymisation. Organisations should establish clear policies and timelines for data retention to ensure GDPR compliance.
Personal data should generally be retained only as long as necessary for processing purposes. However, some data may be retained longer if it serves the public interest or scientific or statistical research, provided proper safeguards are in place. Periodic reviews of stored personal data ensure it is not kept longer than required. This helps maintain compliance and reduce the risk of data breaches.
Data retention periods after consent expires are generally recommended to last from 3 months to 1 year. This range helps ensure compliance and data protection. It is essential to define how long processing continues before re-consenting is necessary. Following these guidelines ensures that data retention and deletion policies comply with GDPR and that data is effectively managed.
Cross-Border Data Transfers
The General Data Protection Regulation aims to ensure that personal data transferred outside the European Economic Area (EEA) receives a level of protection equivalent to that within the EEA. Transfers of personal data to non-EEA countries can occur either based on an adequacy decision or appropriate safeguards. Adequacy decisions confirm that a non-EEA country provides a level of data protection comparable to that in the EEA.
Appropriate safeguards for data transfers may include standard contractual clauses or binding corporate rules. These precautions ensure that the data is protected even when transferred outside the EEA. Without an adequate decision or appropriate safeguards, certain derogations allow for data transfers under specific conditions. Derogations can include scenarios such as explicit consent from the individual or the necessity for contract performance.
Understanding and implementing these mechanisms ensures compliance with GDPR and protects customers’ personal data during cross-border transfers.
Leveraging Contextual Advertising Under GDPR
Contextual advertising offers a GDPR-compliant alternative to traditional user profile-based targeting. This method targets users based on the content they consume rather than their personal data. Focusing on content and user searches, contextual advertising shifts from using personal data to placing ads alongside relevant content.
This approach ensures privacy compliance as it does not rely on cookies or personal data. Using AI, contextual advertising analyses website content and sentiment, ensuring that ads align with the context effectively.
Leveraging contextual advertising allows digital marketers to respect user privacy while delivering relevant and targeted ads.
The Role of Data Protection Officers in Marketing
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) mandates the appointment of a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to ensure resources are directed toward GDPR compliance. A DPO’s primary duty is to guarantee adherence to data protection laws and monitor data protection processes. Organisations are required to involve their DPO in any matters that pertain to the safeguarding of personal data on time.
Failing to appoint a DPO when legally required can lead to penalties, underscoring the importance of compliance. A company can appoint an internal or an external Data Protection Officer, but the internal DPO should not have conflicting interests.
All employees, not just the marketing team, should undergo GDPR compliance training to understand their responsibilities. DPOs must possess specialized knowledge in data protection legislation and IT security to execute their duties effectively.
Ensuring a qualified DPO helps organisations manage their data protection efforts and maintain GDPR compliance.
Practical Steps for GDPR Compliance in Marketing Teams
Digital marketers must record email opt-ins/outs, define data intake processes, and honour data subject requests to align with GDPR responsibilities. To ensure compliance, marketers should follow a specific GDPR checklist designed for their operations. Marketing automation specialists manage tools and software that ensure GDPR compliance during automated marketing processes.
Implementing a single source of truth for consent and managing timely activity related to GDPR compliance using a privacy solution is crucial. Marketers must ensure adequate data protection when transferring personal data to third parties, according to GDPR requirements. Standard contractual clauses or corporate rules can effectively safeguard international data transfers.
A DPO, IT team, and legal experts should review the website’s Privacy Page and Terms & Conditions Page to ensure compliance with GDPR. Offering specific, actionable insights allows digital marketers to effectively disseminate GDPR compliance information and ensure their marketing practices comply.
Summary
Mastering GDPR compliance in digital marketing is not just a regulatory requirement; it’s an opportunity to build trust and enhance your marketing strategies. Marketers can ensure their practices are practical and compliant by understanding the legal bases for processing personal data, obtaining valid consent, respecting data subject rights, and implementing data minimisation principles.
Incorporating GDPR into your digital marketing efforts involves a commitment to transparency, data protection, and responsible data management. By following the practical steps outlined in this guide, compliance can be turned into a competitive advantage. Embrace these practices to foster stronger customer relationships while protecting their data.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary legal bases for processing personal data in marketing under GDPR?
Under GDPR, the primary legal bases for processing personal data in marketing are consent and legitimate interests. Consent must be explicit and specific, while legitimate interests require a clear justification for the marketing objectives.
How can marketers obtain valid consent for marketing purposes?
Marketers must obtain clear, explicit, and granular customer consent, providing transparent information on the reasons for data collection and its intended use. Additionally, it is essential to record and manage this consent effectively.
What rights do data subjects have under GDPR?
Under GDPR, data subjects have rights such as the right to be informed, access their data, rectify inaccuracies, request erasure, and object to processing. These rights enable individuals to exercise control over their personal data.
What is the principle of data minimisation in GDPR?
The principle of data minimization in GDPR mandates that only data adequate, relevant, and necessary for a specific purpose should be collected. This approach helps mitigate risks associated with unlawful processing and data breaches.
How can organisations manage cross-border data transfers under GDPR?
Organisations can manage cross-border data transfers under GDPR by utilising adequacy decisions, implementing appropriate safeguards such as standard contractual clauses or binding corporate rules, and adhering to specific derogations when necessary. This approach ensures compliance while protecting personal data during international transfers.