
Proactive Data Risk Management: A Path to GDPR Compliance
We live in a world where data is a valuable asset, and protecting it has become crucial for businesses. Advanced data risk management is no longer a luxury but a necessity. With regulations like GDPR and CCPA in place, companies need to step up their game to ensure they’re handling sensitive information correctly. We’ve seen how data breaches can damage reputations and lead to hefty fines, making it clear that proper risk assessment and information security are vital for long-term success.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the key aspects of mastering advanced data risk management. We’ll cover the main pillars you need to focus on, dive into GDPR-compliant data processing activities, and discuss how to build a culture of data protection within your organization. By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of how to keep your data safe and your business compliant with current regulations. Let’s get started on this journey to better data protection and risk management.
The Pillars of Advanced Data Risk Management
We’ve found that mastering advanced data risk management involves focusing on three key pillars: data classification and handling, access control and user authentication, and encryption and data masking. Let’s dive into each of these areas to see how they work together to create a robust data protection strategy.
Data Classification and Handling
Data classification is the foundation of effective risk management. It’s about organizing our stored data based on its sensitivity and potential risk. By doing this, we can apply the right security measures and governance controls where they’re needed most.
Here’s how data classification helps us stay GDPR compliant:
1. We can organize data and implement appropriate security controls based on its nature.
2. It’s easier to retrieve consumer data and fulfill data subject requests.
3. We can determine how long to keep data and when to delete it securely.
4. We can spot potential breach risks and act quickly to prevent data threats.
To implement data classification effectively, we need a solid plan. While there’s no one-size-fits-all approach, here are some key steps we should include:
1. Use a data discovery tool to find and categorize our backlog of data.
2. Assign sensitivity levels to each category of personal data.
3. Analyze if our stored data has sufficient security controls.
4. Set up an automated tool for ongoing monitoring and adjustments.
After classification, we need to tailor our data protection measures according to sensitivity and risks. This includes using encryption, setting up access controls, and maintaining accurate records of processing activities (ROPAs).
Access Control and User Authentication
Access control is crucial for cybersecurity. It’s all about regulating who can view, use, or access our resources. By implementing strong access control, we can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and protect our sensitive information.
Here’s why access control is so important:
1. It helps us comply with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
2. It protects against both external attackers and insider threats.
3. It allows us to implement the principle of least privilege, ensuring users only have the access they need.
To implement effective access control, we use a process that involves:
1. Authentication: Verifying the identity of users or systems requesting access.
2. Authorization: Granting or denying access based on predefined privileges.
3. Access: Monitoring and controlling the actual use or interaction with resources.
4. Management: Maintaining and updating the access control system.
5. Auditing: Monitoring and recording access patterns and activities.
We’ve found that Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems play a key role in modern access control strategies. They help us manage the entire user lifecycle, from creating accounts and assigning access to removing access when it’s no longer needed.
Encryption and Data Masking
Encryption and data masking are two powerful tools we use to protect our sensitive data. While they serve different purposes, both are essential for a comprehensive data protection strategy.
Encryption uses complex algorithms to encode our original data into unreadable ciphertext. It’s particularly useful for protecting data at rest and in transit. If our network or system is compromised, or if data transfer is intercepted, encryption makes the data useless to unauthorized users.
Data masking, on the other hand, is ideal for protecting data in use. It replaces sensitive data with fictional or scrambled data that retains the format and appearance of the original. This allows us to use data for development, testing, or analysis without exposing sensitive information.
Here’s how we use these techniques:
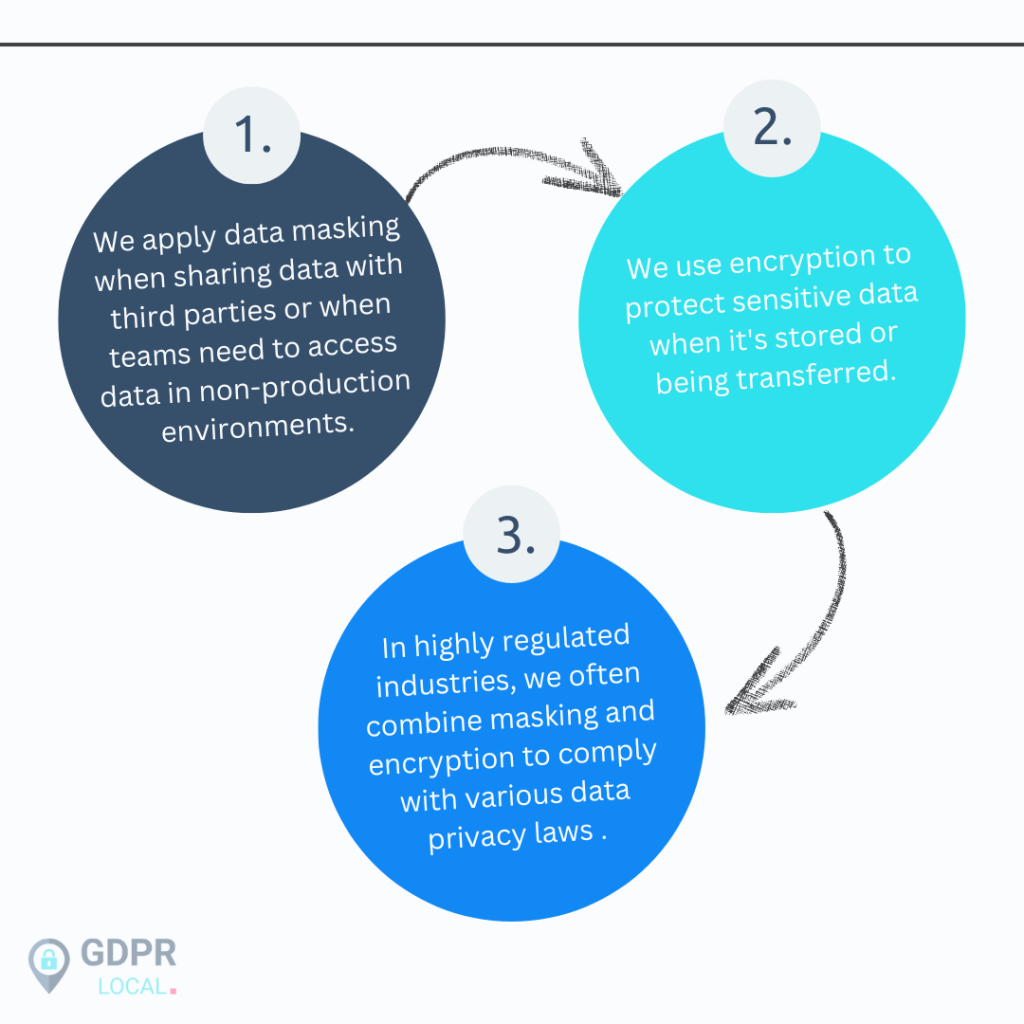
By using a combination of data masking and encryption, we ensure end-to-end protection for our data at rest, in transit, and in use.
Remember, mastering these pillars of advanced data risk management isn’t just about compliance—it’s about building trust with our customers and protecting our organization’s reputation. By implementing these strategies, we’re taking proactive steps to safeguard our most valuable asset: our data.
GDPR-Compliant Data Processing Activities
When it comes to GDPR compliance, we need to pay close attention to our data processing activities. Let’s dive into the key aspects we need to consider to ensure we’re on the right track.
Lawful Basis for Processing
First things first, we need to have a valid lawful basis for processing personal data. The GDPR outlines six lawful bases, and we must choose at least one that applies to our processing activities. These include:
1. Consent from the data subject
2. Necessity for contract performance
3. Compliance with a legal obligation
4. Protection of vital interests
5. Performance of a task in the public interest
6. Legitimate interests pursued by the controller or a third party
It’s crucial to remember that no single basis is more important than the others. We need to choose the most appropriate one based on our purpose and relationship with the individual. Also, if we’re processing special category data or criminal conviction data, we need both a lawful basis and an additional condition.
Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation
Data minimization is a key principle under GDPR. It means we should only collect and process personal data that’s “adequate, relevant and limited to what is necessary” for our specified purposes. In other words, we need to adopt a “less is more” approach.
Here’s why data minimization is so important:
| It reduces costs associated with data storage and processing. |
| It improves processing speed and efficiency. |
| It limits our liability in case of a data breach. |
To check if we’re complying with data minimization, we can ask ourselves these questions:
| Are we only collecting necessary personal data? |
| Do we delete data when it’s no longer needed? |
| Do we regularly review and delete unnecessary data? |
| Do we have a process to ensure we collect and retain the minimum amount of data needed? |
Alongside data minimization, we need to consider purpose limitation. This means we should only process personal data for the specific purpose we collected it for, or for purposes compatible with the original one. If our purposes change, we need to reassess our lawful basis.
Cross-Border Data Transfers
When it comes to transferring personal data outside the EU, we need to be extra careful to ensure GDPR compliance. The first step is to check if the receiving country has an adequacy decision from the European Commission. If it does, we can transfer data without additional safeguards. However, if there’s no adequacy decision, we need to put appropriate safeguards in place.
These safeguards can include:
1. Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs)
2. Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs)
3. Approved codes of conduct
It’s worth noting that the EU-US Privacy Shield, which many organizations relied on for data transfers to the US, was invalidated in July 2020. This means we need to reassess our data transfers to the US and implement alternative safeguards.
Remember, we’re accountable for all the personal data we collect and process. It’s our responsibility to assess our purposes, determine what data we need, and ensure we have the right safeguards in place for any cross-border transfers.
By focusing on these key areas – lawful basis, data minimization, purpose limitation, and cross-border transfers – we can take significant steps towards GDPR-compliant data processing activities. It’s an ongoing process that requires regular review and adjustment, but it’s crucial for protecting both our organization and the individuals whose data we process.
Building a Culture of Data Protection
We’ve found that creating a strong culture of data protection is crucial for GDPR compliance. It’s not just about following rules; it’s about making data protection a part of our everyday work life. Let’s look at how we can build this culture through employee training, the role of a Data Protection Officer (DPO), and ongoing monitoring.
Employee Training and Awareness
Training our team is key to GDPR compliance. We need to make sure everyone understands their role in protecting data. Here’s how we can do it:
1. General Awareness: We should give all our employees basic training on GDPR and their obligations. This includes covering the principles of data protection, data subject rights, and the responsibilities of data controllers and processors.
2. Role-Specific Training: For those who handle personal data regularly, we need to provide more detailed, role-specific training. This should cover the specific procedures and policies relevant to their job.
3. Regular Updates: GDPR training isn’t a one-time thing. We need to keep our team up-to-date with any changes to the regulation or our policies. This helps ensure ongoing compliance.
4. Interactive Workshops: We can use hands-on workshops and simulations to help our team apply GDPR principles in real-world scenarios. This practical approach can really boost understanding and preparedness.
5. Tailored Programs: It’s important to customize our training based on employees’ roles and how much they work with personal data. This ensures everyone gets the right level of education for their job.
Data Protection Officer (DPO) Roles
Appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO) is a crucial step in maintaining GDPR compliance. Here’s what we need to know:
1. DPO Responsibilities: The DPO’s main job is to monitor GDPR compliance. They also provide advice on data protection impact assessments, cooperate with supervisory authorities, and train staff.
2. Independence: It’s important that our DPO can work independently. They shouldn’t receive instructions about how to do their job, and there shouldn’t be any conflicts of interest.
3. Expertise: Our DPO should have expert knowledge of data protection law and practices. They don’t necessarily need to be a lawyer, but they should be able to understand both the technical and legal aspects of data protection.
4. Appointment Criteria: We need to consider the scale and nature of our data processing activities when deciding whether to appoint a DPO. If we process large volumes of personal data or sensitive information, we might be required to have a DPO.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Building a culture of data protection is an ongoing process. We need to keep monitoring and improving our practices:
1. Regular Audits: We should conduct regular audits of our compliance activities. This helps us stay on top of new regulations and best practices.
2. File Integrity Monitoring: Using file integrity monitoring software can give us more control over our data. It can tell us who’s accessing data, alert us to changes, and make it easier to stay GDPR compliant.
3. Staying Informed: With the regulatory landscape constantly evolving, we need to stay informed about new laws and updates. Using a Consent Management Platform (CMP) can help us maintain compliance without overwhelming our team.
4. Record Keeping: We should keep records of all our GDPR training sessions. This helps us demonstrate compliance if we’re ever audited or investigated.
By focusing on these areas, we can create a strong culture of data protection in our organization. Remember, it’s not just about ticking boxes; it’s about making data protection a natural part of how we work.
Conclusion
Mastering advanced data risk management and GDPR compliance has a significant impact on our business’s success and reputation. By focusing on key pillars like data classification, access control, and encryption, we can build a strong foundation to protect sensitive information. These strategies, combined with GDPR-compliant data processing activities, help us to stay ahead of potential threats and maintain the trust of our customers.
Creating a culture of data protection is essential to make these practices stick. Through ongoing employee training, the guidance of a Data Protection Officer, and continuous monitoring, we can make data protection a natural part of our daily operations. This approach not only helps us to comply with regulations but also shows our commitment to safeguarding the personal information entrusted to us. By taking these steps, we’re well-equipped to navigate the complex world of data risk management and privacy regulations.
FAQs
What are the primary requirements of the GDPR?
The GDPR outlines 10 crucial requirements:
1. Lawful, fair, and transparent processing of data.
2. Restrictions on the purpose, extent, and duration of data storage.
3. Rights of data subjects.
4. Obtaining consent from data subjects.
5. Notification and handling of personal data breaches.
6. Implementing Privacy by Design principles.
7. Conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments.
8. Regulation of data transfers across borders.
How can an organization achieve full compliance with GDPR?
To become fully compliant with GDPR, follow these steps:
– Understand and catalog the data you possess.
– Ensure your website is secure.
– Update your privacy policies accordingly.
– Obtain explicit consent for email communications.
– Implement a cookie consent banner on your site.
– Review all web forms for compliance.
– Evaluate your data processors and any third-party services.
– Assess the compliance of your international data transfers.
What steps are involved in obtaining GDPR certification?
To gain GDPR certification, you should:
– Prepare your organization for the certification process.
– Define your policy on personal data management.
– List all activities involving data processing.
– Establish a procedure for managing the rights of data subjects.
– Conduct a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA).
– Ensure the security of personal data during transfers.
Is it compulsory for U.S. companies to comply with GDPR?
Yes, U.S. companies, as well as any company outside the European Union, are subject to GDPR if they process the data of individuals within the EU. The GDPR’s territorial scope under Article 3 mandates compliance irrespective of where the data processing occurs, whether inside or outside the European Economic Area (EEA).