
Understanding the Importance of ISO 27001:2022 Standard
Updated: October 2025
Key Takeaways
• ISO 27001:2022 prevents data breaches by systematically identifying, assessing, and mitigating information security risks across your organisation
• Certification builds trust and opens business opportunities by demonstrating your commitment to information security to customers, partners, and regulatory bodies
• Third-party vendor risks need management – implement ISO 27001 controls to secure your supply chain and prevent breaches through external partners
• GDPR compliance is built in – the standard helps establish robust controls to meet data protection regulations and avoid penalties
Why do you need ISO 27001?
Imagine a scenario where a renowned healthcare provider like Kaiser Permanente notifies over 13 million customers of a potential data compromise due to third-party vendors. Picture individuals receiving unsettling notices detailing the exposure of their personal information, including IP addresses and browsing activity on Kaiser’s website and mobile applications. Despite the absence of financial data or Social Security numbers, the breach raises serious concerns about privacy and data security.
Now, envision another situation where a data broker openly offers the sensitive passport data of thousands of individuals for sale online. Visualise the shock and disappointment of affected individuals upon discovering that their personal information, including names, dates of birth, passport numbers, and expiration dates, is publicly accessible without their consent.
ISO 27001:2022 holds paramount importance in both cases involving Kaiser Permanente’s potential data compromise and the data broker’s sale of sensitive passport data.
Importance of ISO 27001:2022 in Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, such as in Kaiser Permanente’s scenario, ISO 27001:2022 is crucial for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of patient information. Implementing ISO 27001-compliant information security management systems (ISMS) would have helped Kaiser Permanente systematically identify and mitigate risks associated with third-party vendors and online technologies, thereby reducing the likelihood of data breaches and protecting patient privacy.
Importance of ISO 27001:2022 for Data Brokers
Similarly, in the case of the data broker selling passport data, ISO 27001:2022 plays a pivotal role in safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorised access and disclosure. By adhering to ISO 27001:2022 guidelines, organisations can establish robust controls and processes to prevent data breaches and ensure compliance with data protection regulations such as the GDPR. This standard would have aided the data broker in implementing effective security measures to protect the confidentiality and integrity of passport data, ultimately mitigating the risk of identity theft and unauthorised use of personal information.
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, ensuring the security and integrity of sensitive information has become paramount for businesses of all sizes. With cyber threats on the rise and data breaches making headlines, companies must proactively safeguard their data assets to maintain trust and credibility with their stakeholders. This is where ISO 27001:2022 comes into play as a crucial framework for information security management.
ISO 27001:2022 is the latest iteration of the internationally recognised standard, which provides a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information and ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
How to implement ISO 27001 in your company?
But what exactly does this standard entail, and why is it essential for your company?
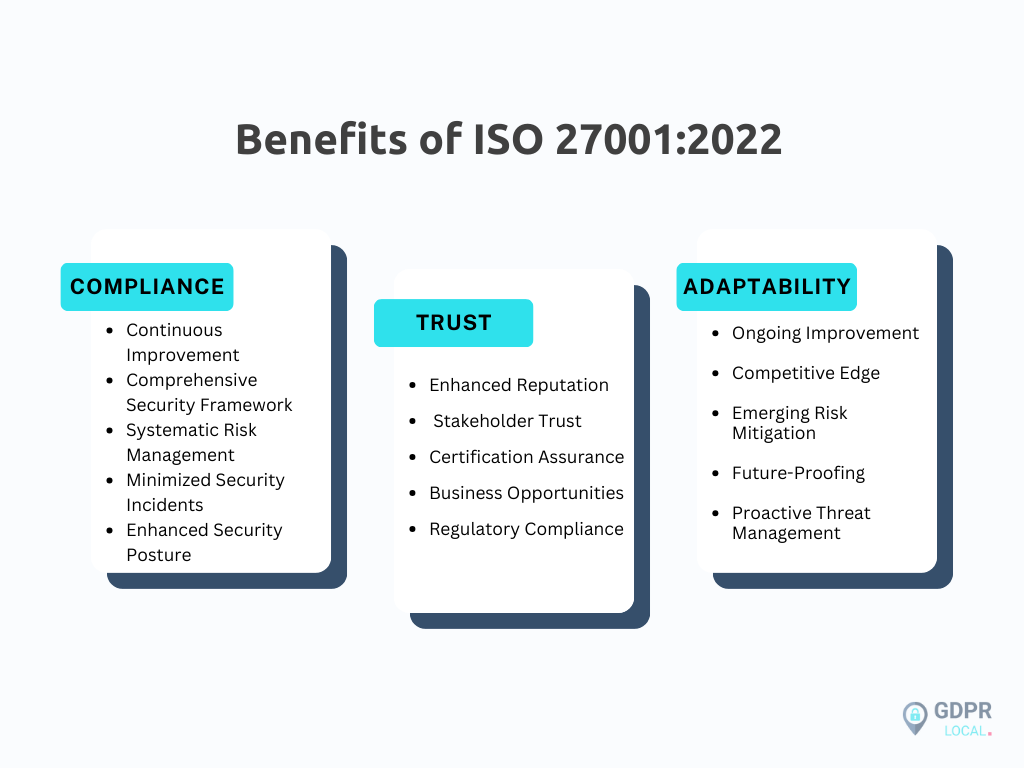
First and foremost, ISO 27001:2022 sets forth a comprehensive set of requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS). This means that by adhering to the guidelines laid out in ISO 27001:2022, your company can systematically identify, assess, and mitigate information security risks, thereby minimising the likelihood of data breaches and other security incidents.
Moreover, ISO 27001:2022 is not just about protecting your company’s internal data—it’s also about demonstrating your commitment to information security to your customers, partners, and regulatory bodies. Achieving ISO 27001 certification signifies to stakeholders that your company takes information security seriously and has implemented robust controls and processes to safeguard sensitive information. This can enhance your reputation, instil trust, and open up new business opportunities, especially when dealing with clients prioritising data security and compliance.
Furthermore, ISO 27001:2022 is a forward-thinking standard that emphasises the importance of adaptability and resilience in the face of evolving cybersecurity threats. By regularly reviewing and updating your ISMS in accordance with the latest best practices and technological advancements, your company can stay ahead of emerging risks and maintain its competitive edge in an increasingly digital marketplace.
How much does ISO 27001 cost?
The cost of implementing ISO 27001 can vary widely depending on your organisation’s size, complexity, and maturity level. For small businesses, the total cost may range from $10,000 to $40,000, while mid-sized and larger companies might spend $50,000 to over $100,000. These costs typically include gap analysis, consultancy, internal training, documentation, risk assessments, technology updates, and certification audits. Certification body fees can range from $5,000 to $20,000, depending on audit duration and company size. It’s also important to factor in ongoing costs for maintaining the ISMS, such as internal audits, surveillance audits (usually annual), and recertification every three years. While the investment may seem high, it often pays off through risk reduction, improved trust, and competitive advantage.
Conclusion
In summary, ISO 27001:2022 is not just a set of guidelines—it’s a strategic investment in your company’s future success and resilience. By implementing the standard’s principles and practices, your company can fortify its defences against cyber threats, enhance its reputation, and foster stakeholder trust. In an era where information security is paramount, ISO 27001:2022 is not just a choice – it’s a necessity for companies striving to thrive in today’s digital age.
FAQ’s:
How long does it take to implement ISO 27001?
Most businesses take between 3 to 12 months to fully implement ISO 27001, depending on their size, resources, and current security posture.
Can a small business implement ISO 27001?
Yes, small businesses can implement ISO 27001. With the right planning and support, even lean teams can build an effective ISMS.
What types of organisations can benefit from ISO 27001?
ISO 27001’s structured security framework can benefit any organisation that handles sensitive data, whether in healthcare, finance, tech, legal, or SaaS.