
GDPR Compliance Checklist: A Practical Guide for Companies
If your organisation handles personal data from EU citizens, GDPR compliance isn’t optional; it’s a necessity. This GDPR compliance checklist provides clear steps to help you conduct data audits, update privacy policies, protect individual rights, and implement strong data security practices.
Key Takeaways
• GDPR compliance requires meeting strict data protection standards applicable to any organisation processing personal data of EU individuals. There are severe penalties for non-compliance.
• Achieving GDPR compliance involves a structured approach, including data audits, appointing a Data Protection Officer, updating privacy policies, and implementing robust security measures.
• Organisations must respect individual rights under GDPR, ensure timely processing of data requests, manage consent effectively, and maintain transparency in data handling practices.
GDPR Compliance
GDPR compliance means meeting the General Data Protection Regulation requirements to protect personal data. This regulation applies to any organisation that processes the personal data of individuals within the European Union, regardless of the organisation’s location. The scope of GDPR is extensive, covering various aspects of data protection and imposing severe penalties for non-compliance, reaching up to £17.5 million or 4% of global annual turnover.
The GDPR outlines seven key data protection principles that guide the processing of personal data: lawfulness, fairness, transparency, purpose limitation, data minimisation, accuracy, storage limitation, integrity, confidentiality, and accountability. These principles form the foundation of data protection compliance and must be followed by organisations acting as data controllers or processors. They are also a foundation for implementing effective data protection policies and maintaining compliance with the regulation.
A thorough understanding of GDPR compliance enables organisations to protect personal data better and avoid significant repercussions of non-compliance.
Steps to Achieve GDPR Compliance
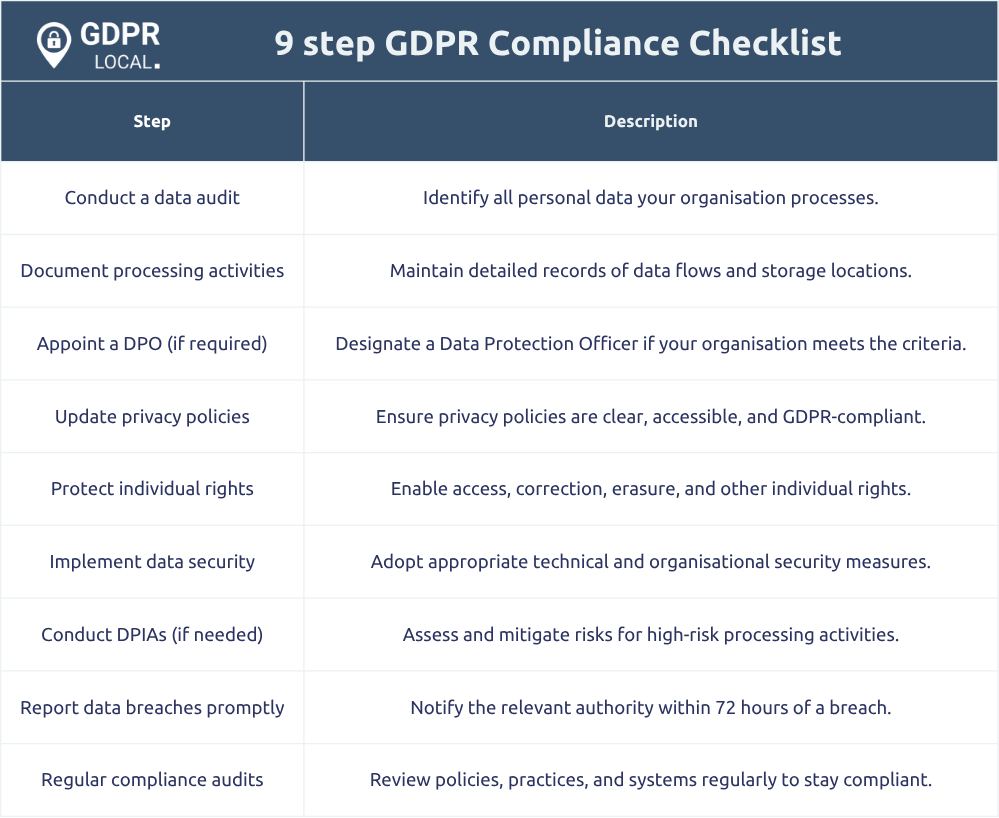
Achieving GDPR compliance requires a methodical approach. Here is a comprehensive nine-step GDPR Checklist designed to ensure all aspects of data protection are addressed:
1. Conduct a data audit to identify all personal data processed by your organisation.
2. Document data processing activities, including data flows and storage locations.
3. Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) if required.
4. Update privacy policies to reflect GDPR requirements.
5. Implement measures to ensure individual rights are protected.
6. Establish robust data security measures.
7. Conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) where necessary.
8. Report data breaches within the stipulated time frame.
9. Conduct regular audits and reviews to maintain compliance.
Knowing your role as a data controller or processor is very important. Regular audits help identify compliance gaps and ensure data protection practices are aligned with evolving regulations.
This compliance checklist provides actionable steps to enhance your organisation’s data protection compliance and mitigate the risks associated with personal data processing.
Data Mapping and Inventory
An information audit is the initial step towards achieving GDPR compliance. This involves identifying all the personal data your organisation processes and ensuring there are legal grounds for processing it. Documenting the types of personal information, such as names, addresses, and social security numbers, is essential. Additionally, you need to document where this information is stored, the sources of the data, any third parties with whom the data is shared, the purpose of processing, and the duration for which the data will be retained.
Grasping data flows and securing data are key components of this process. Thoroughly mapping your data helps identify potential vulnerabilities and implement measures to protect data subjects’ rights. This step lays the foundation for effective data protection compliance and aids in maintaining transparency and accountability in data processing activities.
Appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO)
A Data Protection Officer (DPO) is mandatory for public authorities that regularly monitor individuals or process sensitive data. The DPO’s role includes monitoring GDPR compliance, assessing data protection risks, advising on Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs), and cooperating with regulatory authorities. The DPO should thoroughly understand GDPR guidelines and the organisation’s internal processes involving personal data.
A DPO ensures dedicated oversight of data protection compliance. The DPO maintains the integrity and security of personal data, addresses breaches promptly, and implements data protection policies effectively.
Having a DPO demonstrates your organisation’s commitment to protecting personal data and complying with data protection legislation.
Updating Privacy Policies
Updating privacy policies is a crucial step towards GDPR compliance. Individuals are entitled to clear and concise information about how their personal data is processed, including the purposes and recipients of their data. It’s essential to inform existing customers about changes to your privacy policy, explaining the updates in simple terms.
Update privacy policies regularly to reflect current data protection practices and regulatory requirements. This transparency builds customer trust and demonstrates your organisation’s commitment to data protection compliance.
Clear and updated privacy policies are a cornerstone of adequate data protection and are vital for maintaining GDPR compliance.
Ensuring Individual Rights
One of the cornerstones of GDPR is the protection of individual rights. Under GDPR, individuals can access their data, know how long it will be stored, and request its deletion. They are entitled to transparent information about collecting and processing their data. They can request to have their personal data deleted, a request that must be honoured within one month. Organisations must notify individuals before processing data again after a restriction request.
Organisations must comply with data subject requests, such as stopping data processing, within a stipulated time frame. These rights ensure that individuals have control over their personal data and can hold organisations accountable for their data use.
Respecting individual rights is a legal obligation and a cornerstone of ethical data management.
Handling Data Subject Requests
Efficient handling of data subject requests is vital for GDPR compliance. Organisations must ensure they have defined processes to verify the identity of individuals making data requests. This verification is essential to prevent unauthorised access to personal data.
Additionally, organisations must establish clear procedures for customers to access or modify their data. Robust processes enable prompt and accurate responses to data subject requests, ensuring GDPR compliance and maintaining customer trust.
Managing Consent
Consent management is a fundamental aspect of GDPR compliance. Consent for data processing should be freely given, specific, informed, and revocable. This means that individuals must be fully aware of what they are consenting to and should be able to withdraw their consent at any time without any complications.
Consent must be informed and specific to the circumstances, particularly when dealing with sensitive data or special categories of data from minors. Organisations must ensure that they have clear records of consent and that these records are easily accessible.
Proper consent management helps organisations ensure compliance and protect the rights of data subjects.
Implementing Data Security Measures
Robust data security measures are essential to protect personal data against unauthorised access and breaches. A comprehensive security policy covering email security, password management, two-factor authentication, VPN usage, and technical security is critical. Techniques such as encryption, minimising the collection of personal data, and ensuring the deletion of unneeded data are vital organisational measures for data protection.
Organisations must implement appropriate measures to demonstrate compliance with GDPR. Assigning clear accountability for GDPR compliance ensures that someone oversees adherence to data protection regulations and the supervisory authority.
Effective data security measures protect personal data and enhance the business organisation’s reputation and trustworthiness.
Conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs)
Conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) is necessary for organisations engaged in extensive data processing or profiling that poses a high risk to individuals’ rights. A DPIA identifies and mitigates risks associated with determining data handling practices.
Conducting DPIAs allows organisations to address potential data protection risks and ensure GDPR compliance proactively. This practice identifies vulnerabilities and reinforces the commitment to data protection compliance.
Reporting Data Breaches
Organisations must inform relevant authorities and affected individuals within 72 hours of a data breach to avoid undue delay. This prompt reporting is crucial for mitigating the impact of the breach and ensuring transparency.
Clear procedures for reporting data breaches, including contact points and communication methods, must be in place. Timely reporting aids in effective breach management and demonstrates a commitment to data protection compliance.
Accountability and Governance
Accountability and governance are essential for maintaining GDPR compliance. The board should assign someone accountable for GDPR compliance, ensuring clear leadership and responsibility. Board-level support is crucial for allocating necessary resources and understanding the implications of GDPR.
Good information handling practices enhance reputation and confidence, which is essential for GDPR compliance. Regular assessments of third-party services are also necessary to uphold GDPR compliance and manage privacy risks effectively.
Assigning accountability provides clear ownership of responsibilities, facilitating the implementation and maintenance of data protection measures.
Training Employees
Training employees on GDPR principles and the importance of safeguarding personal data reduces the risk of breaches caused by human error. Providing GDPR training helps employees understand their responsibilities regarding data protection.
Effective training programs contribute to overall GDPR compliance and build a culture of data protection. By educating employees, organisations can foster an environment where data protection is a shared responsibility, thereby mitigating risks and enhancing compliance.
Regular Audits and Reviews
Regular audits and reviews are crucial for maintaining GDPR compliance. Organisations must stay informed about best practices for GDPR compliance and monitor any changes to local policies related to this regulation. Regular reviews of policies for changes, effectiveness, data handling, and international data flow are crucial for ensuring ongoing compliance.
Thorough audits of procedures and practices help assess risks related to personal information management. Regular audits of third-party vendors ensure ongoing compliance with GDPR requirements. These practices help organisations stay compliant and address any potential issues proactively.
Third-Party Data Processors
Managing third-party data processors is critical for ensuring GDPR compliance. Organisations must maintain clear contracts with third-party processors, outlining data protection responsibilities and compliance obligations. The processors’ checklist includes requirements for processors, rights of individuals, and procedures for data breaches.
Regular assessments of third-party service providers uphold GDPR compliance and effectively manage privacy risks. By managing third-party relationships carefully, organisations can mitigate risks and ensure that their data protection practices align with GDPR requirements.
Data Processing Agreements
Data processing agreements should clearly outline the roles and responsibilities of both the data controller and the processor and include specific clauses about data breaches, confidentiality, and the rights of data subjects.
Ensuring third parties have adequate technical and organisational measures to safeguard personal data is essential for compliance. Clear agreements prevent compliance issues and clarify the relationship between data controllers and processors.
Monitoring Compliance
Continuous monitoring of third-party data processors ensures ongoing compliance with GDPR requirements. Key performance indicators (KPIs) help organisations monitor third-party compliance with GDPR.
Regular assessments and audits of third-party service providers uphold GDPR compliance and effectively manage privacy risks. Systematic monitoring of compliance allows organisations to mitigate risks and ensure their data protection practices align with GDPR requirements.
Direct Marketing Compliance
Direct marketing, including promotional and sales activities, must comply with GDPR. Businesses should assess the Privacy and Electronic Communications Regulation (PECR) alongside data protection legislation to ensure they meet all regulatory requirements. Types of direct marketing include telephone, email, text, and postal marketing.
Data subjects must be able to easily withdraw their consent for marketing communications at any time in an easily accessible form. Clear and plain language opt-out mechanisms help maintain compliance and build trust with your audience.
Regular reviews and updates of direct marketing practices ensure that communications remain GDPR compliant and respect individuals’ rights.
Summary
In summary, achieving GDPR compliance is a multifaceted process that requires a thorough understanding, careful planning, and diligent execution. By following this comprehensive checklist, organisations can ensure they meet all regulatory requirements, protect personal data, and uphold the rights of individuals. Each step is crucial for maintaining compliance, from conducting data audits and appointing a Data Protection Officer to updating privacy policies and implementing robust data security measures.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is GDPR compliance, and why is it important?
GDPR compliance entails adhering to the General Data Protection Regulation to protect personal data. It is vital for protecting data, avoiding hefty penalties, and fostering trust with customers and stakeholders.
What steps should an organisation take to achieve GDPR compliance?
To achieve GDPR compliance, organisations must conduct data audits, document processing activities, appoint a Data Protection Officer, and update privacy policies. Implementing data security measures and regularly conducting audits are essential to maintaining compliance.
When is a Data Protection Officer (DPO) required?
A Data Protection Officer (DPO) is required for public authorities, organisations that conduct large-scale monitoring of individuals, or those that process sensitive data extensively. This ensures compliance with data protection regulations.
How should organisations handle data subject requests?
Organisations should implement defined processes for verifying the identity of individuals making data subject requests and establish clear procedures for customers to access or modify their data. This approach ensures compliance and protects individuals’ privacy rights.
What are the requirements for direct marketing compliance under GDPR?
Direct marketing under GDPR requires data subjects to withdraw their consent for communications easily, and businesses must regularly review their practices to comply with GDPR and PECR regulations.